齐鲁师范学院
- 已知系统的开环传递函数为
 ,则(—2,j0)点在根轨迹上。( )
,则(—2,j0)点在根轨迹上。( ) - 实轴上的某一区域,若其右边开环实数极点个数之和为奇数,则该区域必是根轨迹。( )
- 系统的瞬态性能通常以系统在零初始条件下,对单位阶跃输入信号的响应来衡量。( )
- 已知-2+j0点在开环传递函数为
 的系统的根轨迹上,则该点对应的k值为2 。( )
的系统的根轨迹上,则该点对应的k值为2 。( ) - 设某系统开环传递函数为sys=tf(10,conv([1 1 10],[1 1])),则其频率特性奈氏图起点坐标为(1,j0)。( )
- 如果要求系统的快速性好,则开环极点应距离虚轴越远越好。( )
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/161dfeac7f3a4ab7812aa866dbdad4bd.png
- 系统特征方程式的所有根均在s平面的左半部分是系统稳定的充要条件。( )
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/2930c0b5cccd4187ab2ed11aaa34bb82.png
- 线性定常系统的传递函数定义:系统的输出量的拉氏变换与输入量拉氏变换之比。( )
- 系统的递函数 .w64852252134s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252134s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252134s .pen1 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 19; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252134s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252134s .font1 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252134s .font2 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252134s .font3 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252134s .font4 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } 1 () 1 Φ s s = + ,若输入信号为 .w64852252117s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252117s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252117s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252117s .font1 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252117s .font2 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252117s .font3 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } ()sin rtt = ,则系统的稳态输出 .w64852252156s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252156s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252156s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252156s .font1 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252156s .font2 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252156s .font3 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } () ct = .w64852252135s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252135s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252135s .pen1 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252135s .brush1 { fill: rgb(0,0,0); } .w64852252135s .pen2 { stroke: none; } .w64852252135s .pen3 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 19; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252135s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252135s .font1 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252135s .font2 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252135s .font3 { font-size: 282px; font-family: "MT Extra", serif; } .w64852252135s .brush2 { fill: rgb(0,0,0); } .w64852252135s .font4 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } 2 sin(45) 2 t - o 。( )
- 闭环零点由开环前向通路传递函数的零点和反馈通路传递函数的极点组成。( )
- 以下关于数学模型的描述,正确的是( )
- 描述系统动态过程特征的动态性能指标中,可用来评价系统响应速度的指标有( )。
- 控制系统校正方法有( )
- 决定二阶系统动态性能的两个重要参数是( )。
- 方框图的基本连接方式有( )。
- 若两个系统的根轨迹相同,则有相同的( )
- 确定根轨迹与虚轴的交点,可用( )确定。
- 开环传递函数为
 ,则实轴上的根轨迹为( )。
,则实轴上的根轨迹为( )。 - 信号流图中,( )的支路称为阱节点。
- 以下二阶系统的阶跃响应曲线中,阻尼比ξ=0的系统是( )。
- 对于欠阻尼的二阶系统,当阻尼比ξ保持不变时,( )。
- 已知系统开环传递函数,用MATLAB命令描述为:sys=tf(2,[16,10,1]); .w64852252144s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252144s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252144s .font0 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252144s .font1 { font-size: 242px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252144s .font2 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252144s .font3 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252144s .font4 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } = - + R N N , , ( )。
- 线性系统的频率特性( )。
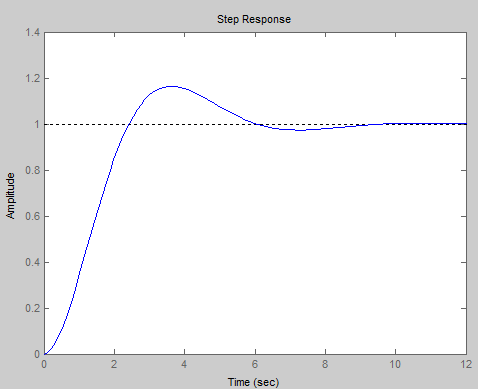
- 以下二阶系统的阶跃响应曲线中,阻尼比ξ<0的系统是( )。
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/c3c2ec1723cd4b8eb106734bf739bd96.png
- 以下MATLAB命令中,用来求单位阶跃响应的是( )。
- 设 .w64852252149s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252149s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252149s .font0 { font-size: 464px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252149s .pen1 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 19; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252149s .font1 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252149s .font2 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252149s .font3 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252149s .font4 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } ( ) ( ) ()() 12 k GsHs ss = ++ ,当k增大时,闭环系统( )。
- 工程上习惯于把过渡过程调整为( )过程。
- 典型欠阻尼二阶系统,当开环增益K增加时,系统( )。
- 信号流图中,( )的支路称为混合节点。
- 积分环节的幅频特性,其幅值和频率成( )。
- 利用MATLAB命令:sys=tf([6 18],[1 2 2])描述系统的闭环传递函数,则该系统单位阶跃响应的模态有( )。
- 设开环传递函数为 .w64852252128s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252128s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252128s .pen1 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 19; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252128s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252128s .font1 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252128s .font2 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252128s .font3 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } () (1) k Gs ss = + ,在根轨迹的分离点处,其对应的 .w64852252171s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252171s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252171s .font0 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252171s .font1 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } k 值应为( )。
- 设某系统开环传递函数用MATLAB表示为sys=tf([1],[2 3 1 0]),则其频率特性的极坐标图与负实轴交点的频率值 .w64852252153s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252153s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252153s .font0 { font-style: italic; font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252153s .font1 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } w 为( )。
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/60618e93cdb24d139bc7f9d8a6ea17f8.png
- 输出信号与输入信号的相位差随频率变化的关系是( )。
- 典型的积分环节的传递函数为( )
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/5ef5432b5d4d4b2b9a70ba0eaca1948d.png
- 若二阶系统的单位阶跃响应为发散正弦振荡,则系统具有( )。
- 一阶系统的闭环极点越靠近 .w64852252166s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252166s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252166s .font0 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252166s .font1 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } s 平面原点,其( )。
- 典型的微分环节的传递函数为( )
- 已知单位反馈系统的开环传递函数用MATLAB命令描述为:sys=zpk([],[0,-2],5),则其根轨迹增益K*等于( )
- 设积分环节的频率特性为 .w64852252116s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252116s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252116s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252116s .font1 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252116s .font2 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252116s .font3 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252116s .font4 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 80px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } (j ω )1/(j ω ) G = ,当频率 .w64852252164s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252164s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252164s .font0 { font-style: italic; font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252164s .font1 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } w 从 .w64852252143s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252143s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252143s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252143s .font1 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252143s .font2 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } 0 ®¥ 时,其坐标平面上的奈奎斯特曲线是( )。
- https://image.zhihuishu.com/zhs/question-import/formula/202203/db55b67644c540adabebc683c1f15422.png
- 某单位反馈系统开环传递函数用MATLAB描述为:sys=zpk([-1,-0.5],[0,0,-10,-5],100),当输入为单位加速度信号时,系统稳态误差为( )。
- 一阶系统sys=tf(K,[T,1])的放大系数K越小,则系统的输出响应的稳态值( )。
- 已知单位负反馈系统的开环传递函数 .w64852252152s .brush0 { fill: rgb(255,255,255); } .w64852252152s .pen0 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 1; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252152s .pen1 { stroke: rgb(0,0,0); stroke-width: 16; stroke-linejoin: round; } .w64852252152s .font0 { font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252152s .font1 { font-size: 373px; font-family: Symbol, serif; } .w64852252152s .font2 { font-style: italic; font-size: 406px; font-family: "Times New Roman", serif; } .w64852252152s .font3 { font-weight: bold; font-size: 76px; font-family: System, sans-serif; } ) 2 )( 1 ( 2 ) ( + + = s s s s G ,通过MATLAB命令[a,b,c,d] = margin(num,den),可得到运行结果:a=3.0000,b=32.6133,c=1.4142,d=0.7494。则该系统幅值裕度为( )。
- 利用MATLAB命令sys=parallel(sys1,sys2)化简方框图时,sys1和sys2是哪种连接方式( )
A:错 B:对
答案:错
A:对 B:错
答案:A: 对
A:错 B:对
答案:对
A:对 B:错
答案:对
A:对 B:错
答案:对
A:错 B:对
答案:A: 错 快速性好通常意味着系统响应快,但这并不一定意味着开环极点应该距离虚轴越远越好。实际上,如果开环极点离虚轴太远,可能会使得闭环系统的响应变得非常快以至于难以控制,甚至可能导致系统不稳定。正确的做法是根据具体的设计要求来确定合适的极点位置。
A:错 B:对
答案:
A:对 B:错
答案:对
A:对 B:错
答案:
A:错 B:对
A:错 B:对
A:对 B:错
A:信号流图不是数学模型的图示 B:系统数学模型的建立方法有解析法和实验法两类 C:数学模型是描述系统输入、输出变量以及系统内部各变量之间的动态关系的数学表达式 D:常用的数学模型有微分方程、传递函数及状态空间表达式等
A:峰值时间 B:超调量 C:上升时间 D:调节时间
A:反馈校正 B:前馈校正 C:复合校正 D:串联校正
A:时间常数T B:自然振荡角频率
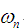 C:比例系数K
D:阻尼比ξ
C:比例系数K
D:阻尼比ξ
A:串联连接 B:并联连接 C:反馈连接 D:顺序连接
A:闭环极点 B:闭环零点 C:开环极点 D:开环零点
A:幅值条件 B: C:劳斯判据 D:幅角条件
A:[-1,∞] B:[-3,-1] C:(-∞,-3] D:[0,∞)
A:只有信号输出 B:只有信号输入 C:既有信号输入又有信号输出 D:任意
A:
 B:
B: C:
C: D:
D:
A:无阻尼自然振荡频率越大,系统的峰值时间不定 B:无阻尼自然振荡频率越大,系统的峰值时间越大 C:无阻尼自然振荡频率越大,系统的峰值时间越小 D:无阻尼自然振荡频率越大,系统的峰值时间不变
A:0,1,-2 B:0,0.5,-1 C:0,0,0 D:1,1,0
A:由系统的结构、参数确定 B:与输入幅值有关 C:与输出有关 D:与时间 有关
A:
 B:
B: C:
C: D:
D:
A:0.5 B:3 C:1 D:0.25
A:impulse() B:lsim() C:step() D:initial()
A:始终不稳定 B:由不稳定到稳定 C:由稳定到不稳定 D:始终稳定
A:欠阻尼 B:过阻尼 C:无阻尼(或临界稳定) D:临界阻尼(或临界振荡)
A:阻尼比
 减小,超调量
减小,超调量 增大;
B:无阻尼自然频率
增大;
B:无阻尼自然频率 减小。
C:阻尼比
减小。
C:阻尼比 增大,超调量
增大,超调量 增大;
D:阻尼比
增大;
D:阻尼比 增大,超调量
增大,超调量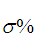 减小;
减小;
A:既有信号输入又有信号输出 B:任意 C:只有信号输入 D:只有信号输出
A:不定关系 B:指数关系 C:正比关系 D:反比关系
A:
 B:
B: C:
C: D:
D:
A:1 B:0.5 C:4 D:0.25
A: B: C: D:
A:
 B:
B: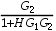 C:
C: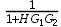 D:
D:
A:相频特性 B:幅频特性 C:频率响应函数 D:传递函数
A:
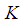 B:
B: C:S
D:
C:S
D:
A:增大 B:不变 C:减小 D:不定
A:两个负实部的特征根 B:一对纯虚根 C:两个正实部的特征根 D:两个正实根
A:响应速度越快 B:响应速度越慢 C:准确度越低 D:准确度越高
A:
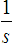 B:
B: C:
C: D:S
D:S
A:2.5 B:3 C:5 D:1.5
A:正虚轴 B:负虚轴 C:正实轴 D:负实轴
A:10 B:30 C:20 D:40
A:1 B:10 C: D:0
A:不定 B:越小 C:不变 D:越大
A:0.7494 B:1.4142 C:3.0000 D:32.6133
A:负反馈 B:正反馈 C:并联 D:串联
温馨提示支付 ¥5.00 元后可查看付费内容,请先翻页预览!

