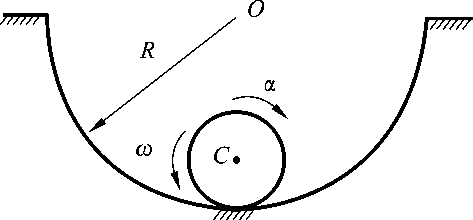
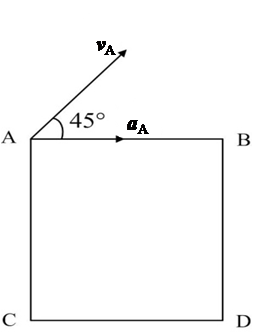
- Given that the rigid body is doing plane motion, at a instant, the acceleration of a point O on the plane figure is aO, the angular acceleration is α, and the angular velocity is ω=0, then the acceleration direction of each point on the line passing through O and perpendicular to aO must be perpendicular to this line.( )
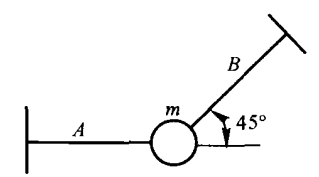
- The direction of the constraint reaction force is always the same as the direction of motion of the constrained object prevented by the constraint. ( )
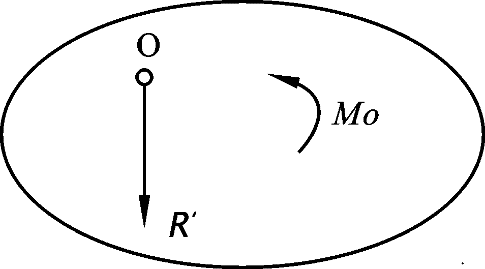
- The principal vector of a conplanar force system simplified to a point is zero, and the principal moment is not zero. Then the force system can be simplified to a resultant couple, and the principal moment of the force system simplified to any point is independent of the position of the simplified center. ( )
- A rigid body rotates about a fixed axis, if the angular acceleration is positive, the rigid body is accelerating. If the angular acceleration is negative, the rigid body is decelerating.( )
- When a point moves in a curve, given velocity v1 at instant t1 and v2 at instant t2, the average acceleration of the point over the time interval t1 to t2 is (v2- v1)/( t2- t1).( )
- A particle slides in a rough horizontal groove, if the initial velocity acquired by the particle is just enough to let it rotate once in the circular groove, the work done by the kinetic friction is equal to zero.( )
- When a wheel moves in a straight track, the work done by friction is zero. ( )
- The acceleration of each point on any line parallel to the rotational axis of a rotating rigid body is equal in magnitude and direction.( )
- A particle moves once around a closed curve. If the force acting on a particle is a potential force, the work done by the force is zero.( )
- Kinetic energy equals work.( )
- The internal force of a particle system cannot change its momentum and angular momentum.( )
- In any case, the magnitude of friction is always equal to the product of the coefficient of friction and the normal reaction force.( )
- The velocity vectors of all points on a plane figure are equal only if the angular velocity of the plane figure is zero.( )
- A couple can only affect the rotation of a free rigid body, but not the motion of its center of mass.( )
- When a rigid body rotates around a fixed axis, the angle between the total acceleration and the normal acceleration of all points in the body is always the same.( )
- Translation and fixed-axis rotation of rigid body are both special cases of plane motion of rigid body.( )
- When the motion of a point is studied by natural coordinate system, the projection of the acceleration on the binormal must be zero.( )
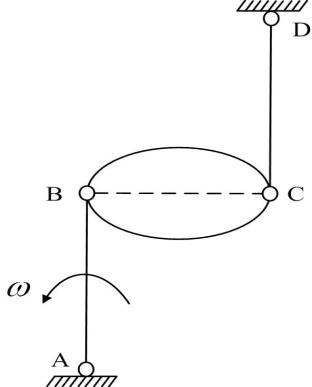
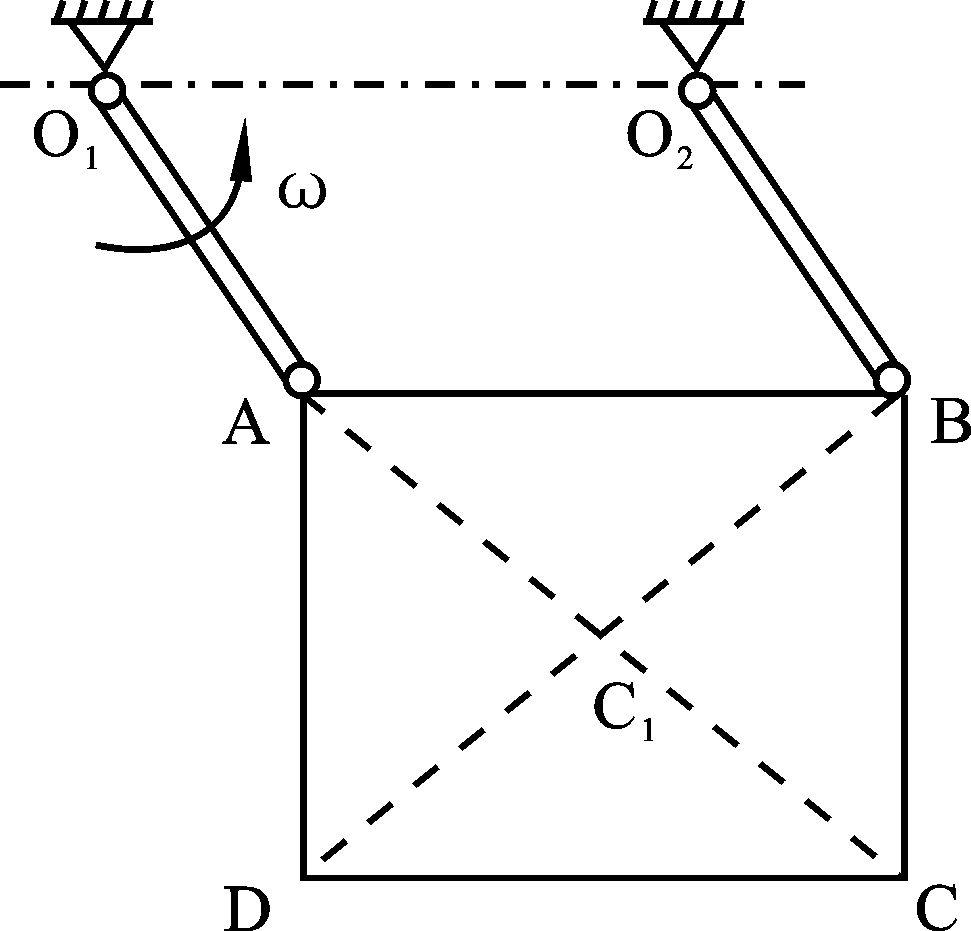
- The plane motion of a rigid body can be divided into two parts by using the method of base point, namely, translation with the base point and rotation about the base point. The angular velocity is the relative angular velocity of the rigid body around the base point, which is also equal to the absolute angular velocity of the rigid body.( )
- A point moves along its trajectory, if v//a at certain instant, then the point must move in a straight line.( )
- A rigid body rotates about a fixed axis, and the moving point M moves along a straight line parallel to the rotational axis in the rigid body. If the moving coordinate system is attached to the rigid body, the transport acceleration of moving point at any instant is identical.( )
- The kinetic energy of a rigid body in plane motion is the sum of the kinetic energy of the rigid body moving with any base point and the kinetic energy of the rigid body rotating about the axis passing through the base point perpendicular to the plane of motion.( )
- When the transport motion is translation, the relative acceleration is equal to the first derivative of the relative velocity with respect to time.( )
- The direction of friction is always opposite to the direction of motion.( )
- Under any initial conditions, if a rigid body is subjected to no force, it should remain stationary or translational in a straight line at constant velocity. ( )
- If the normal acceleration of a moving point is equal to zero at an instant, but its tangential acceleration is not, then it is not clear whether the point moves in a straight line or in a curve. ( )
- In studying the composite motion of the point, the selected moving point must be in motion with respect to the earth. ( )
- There is no Coriolis acceleration when the transport motion is translation, but there must be coriolis acceleration when the transport motion is rotation around the fixed axis. ( )
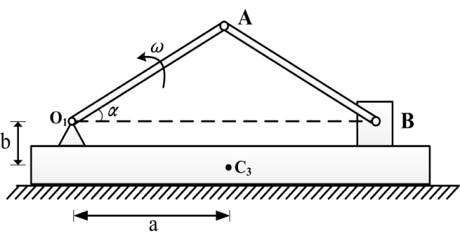
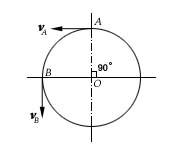
- A rigid body is in plane motion, and points A and B are any two points on it. At the instant when the rigid body is doing instantaneous translation, which following statement is true? ( )
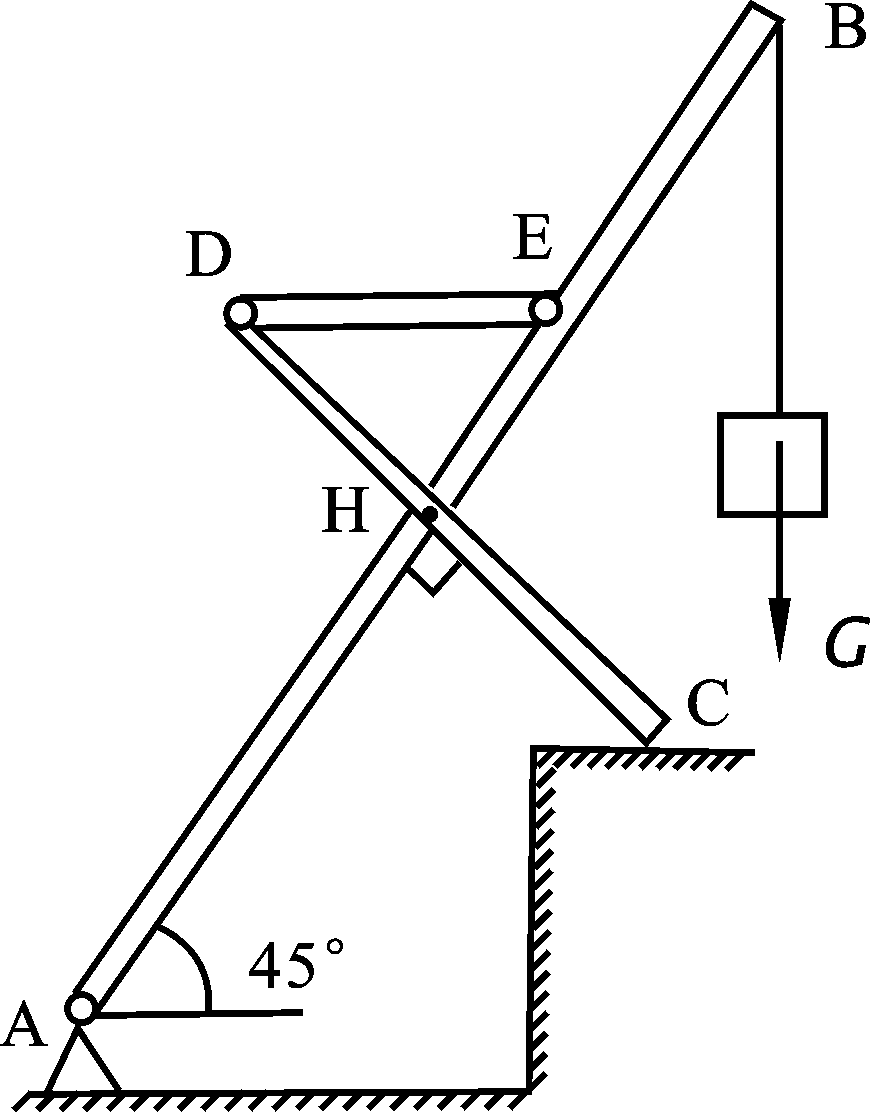
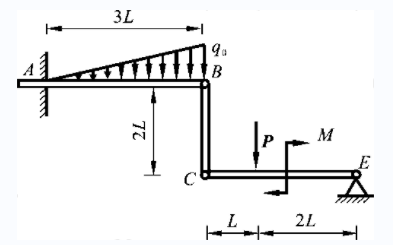
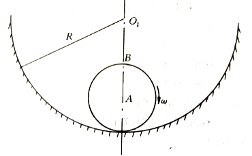
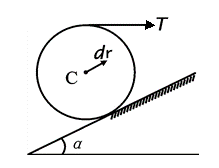
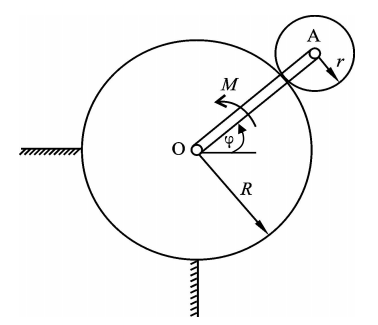
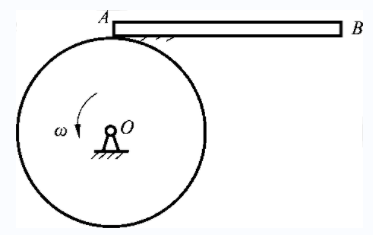
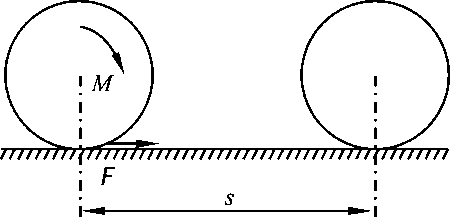
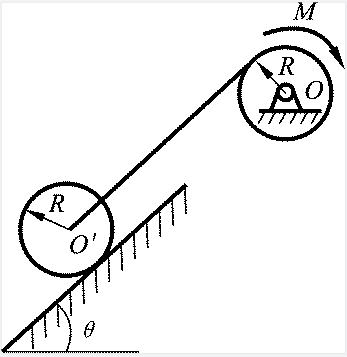

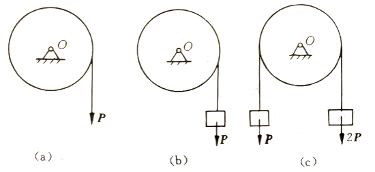
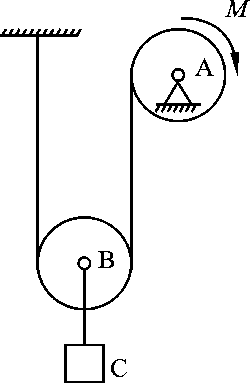
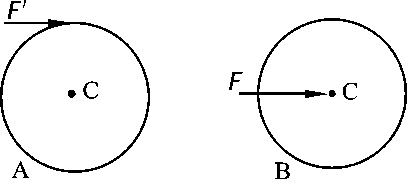
- If the principal moment of the external force acting on the particle system is not zero for the fixed point O, the angular momentum of the particle system for O must not be conserved. ( )

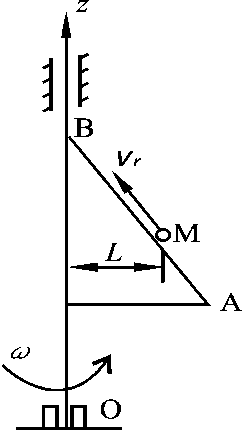
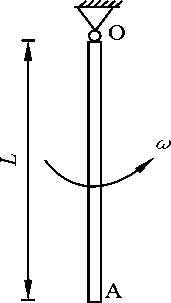
- A homogeneous rod OA rotates around the fixed axis O with constant angular velocity ω. The mass of the rod is m and its length is L, then the magnitude of momentum of this rod is mLω/2.
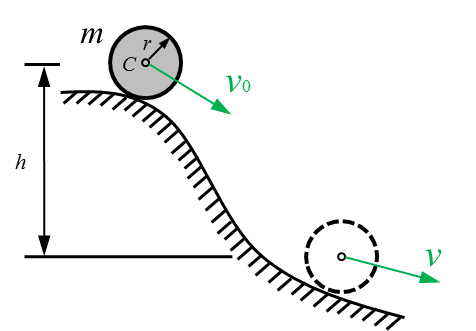
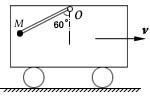
- If two particles have the same mass and are acted upon by the same force, their velocities and accelerations are equal at any instant. ( )
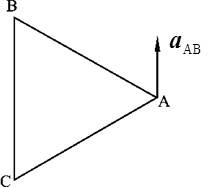
- The acceleration of the instantaneous center of velocities may also be zero. ( )
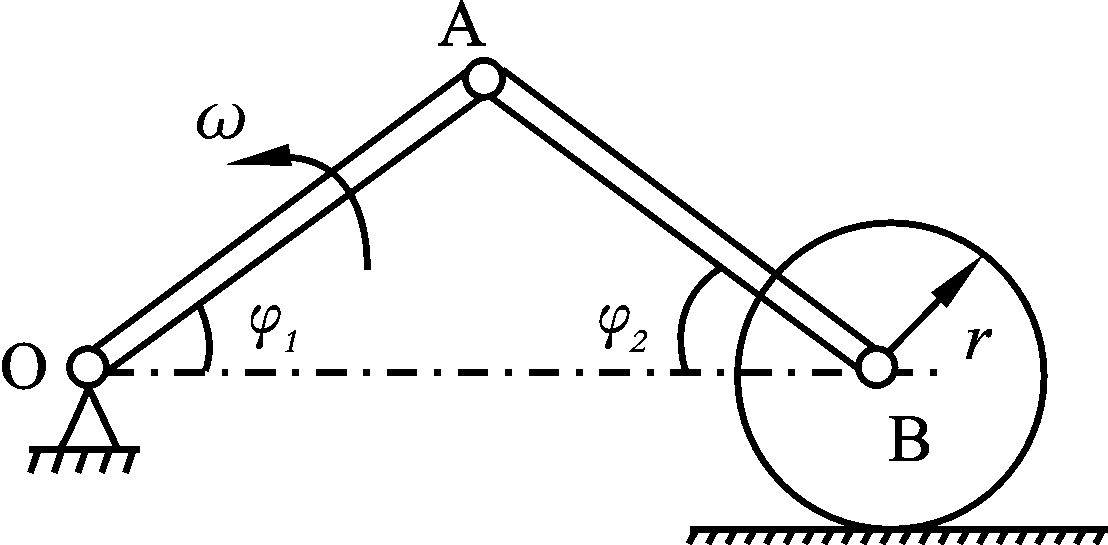
- If the velocity of a moving point which is doing plane curvilinear motion is constant, the velocity vector is perpendicular to the acceleration vector. ( )
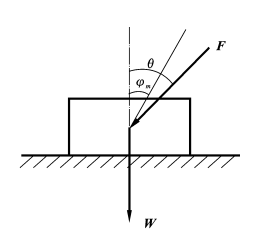
- In the case of friction, the angle between the total reaction force and the normal reaction force is called the angle of friction. ( )

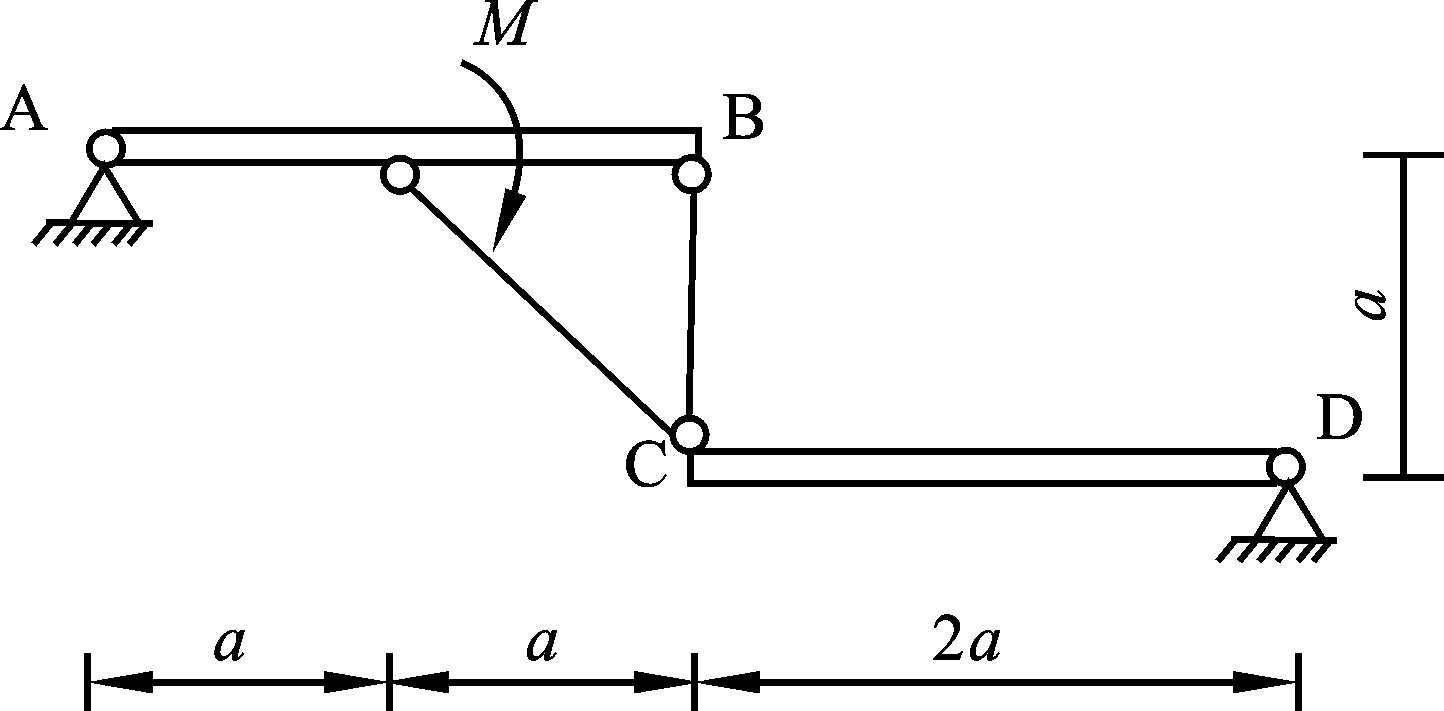
- There are at most three independent equilibrium equations for a noncoplanar force system in which each force action line is perpendicular to a fixed plane. ( )
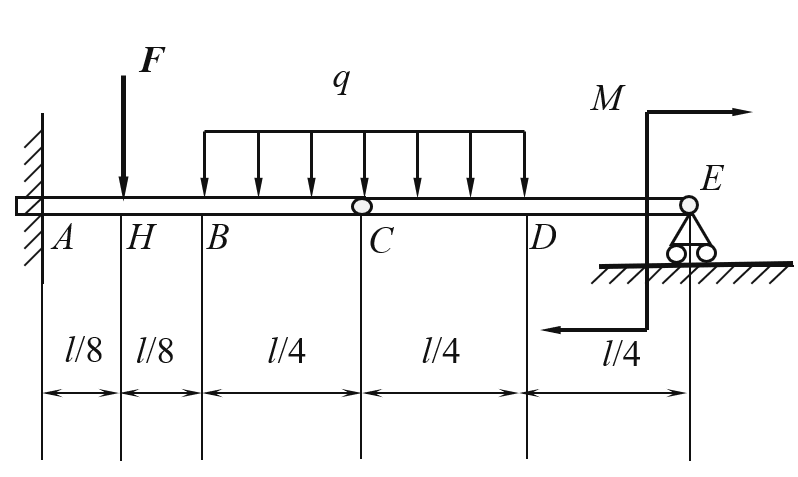
- There are five independent equilibrium equations for a noncoplanar force system in which the action lines of the forces are on two parallel fixed planes. ( )

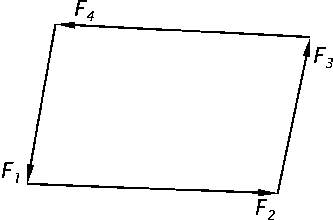
- Taking any two points A and B in the action plane of the conplanar force system, if the principal moments of the force system about these two points are both zero, the force system cannot be composed into a force. ( )
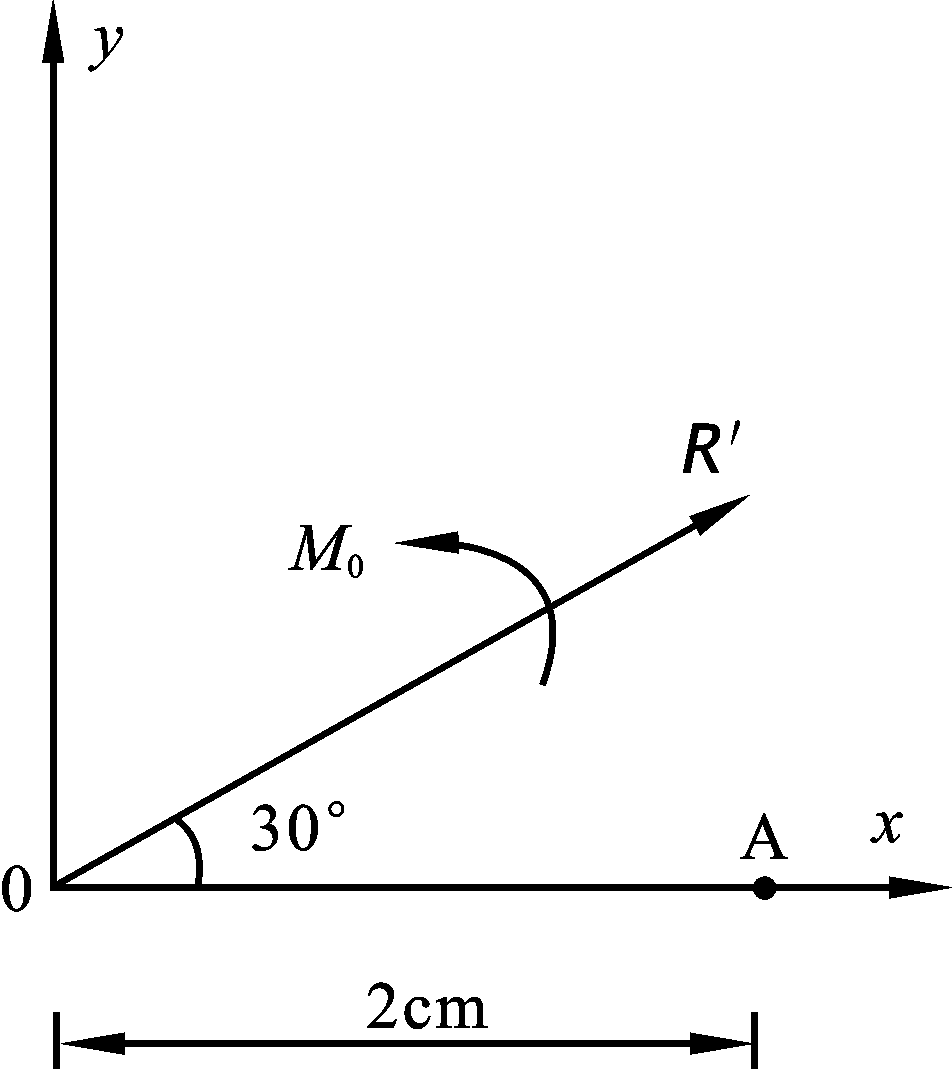

- A conplanar force system cannot be composed into a couple if the principal moment of the force system about any point is equal to zero. ( )

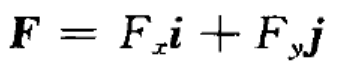
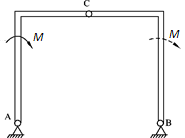
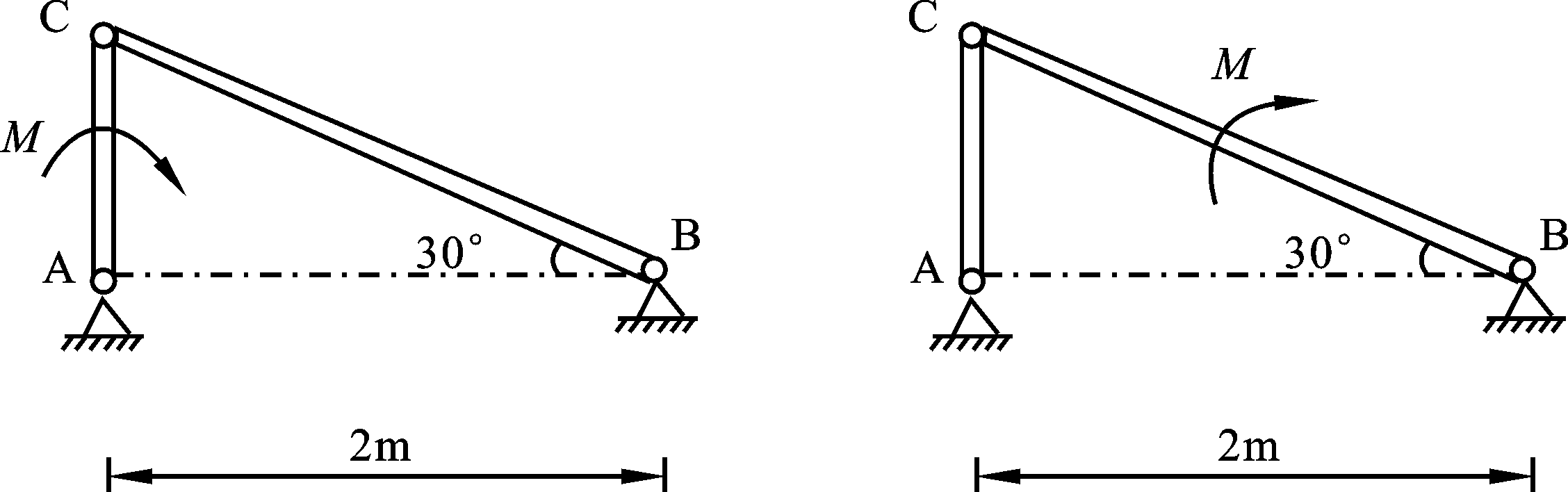

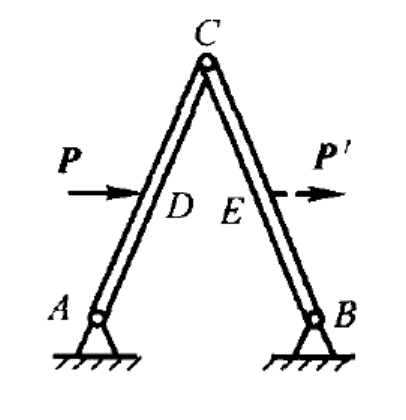
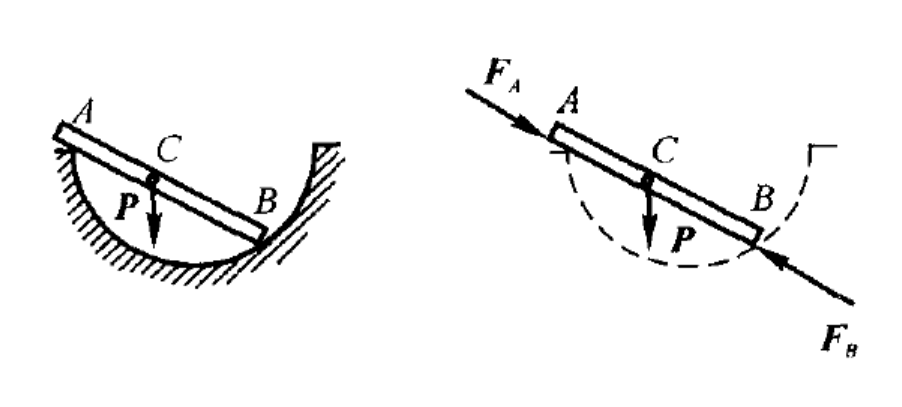
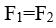
- A rigid body, subjected to forces which are acted on two points, is called Double-force Body. ( )
- After the 20th century, physics divided into two branches: modern physics and modern mechanics.( )
- Who is known as the "father of mechanics"( ).
答案:对
答案:错
答案:对
答案:错
答案:错
答案:错
答案:错
答案:对
答案:对
答案:错
答案:对
温馨提示支付 ¥5.00 元后可查看付费内容,请先翻页预览!







