上海财经大学浙江学院
- Which of the following could be included in a time series based sales forecast?( )(i) Trend(ii) Seasonal variation(iii) Cyclical variation(iv) Random fluctuation
- A company employs three drivers to deliver goods to its customers. The salaries paid to these drivers are: ( )
- Which of the following items might be a suitable cost unit within the accounts payable department of a company? ( )(i) Postage cost (iii) Supplier account(ii) Invoice processed
- A company has 4,000 staff at the start of 20X6 and at the end this had reduced to 3,800due to redundancies being made. 210 staff took voluntary redundancy which was 10 morethan the company had anticipated and these 10 employees were replaced.What is the labor turnover rate per year? ( )
- which of the following explains the essence of quota sampling?( )
- Good quality saves money but the cost of quality can be analysed into cost of conformance and cost of non-conformance. Which one of the following costs is classed as a quality-related appraisal cost? ( )
- Over a period, a firm made purchases of $800, $1,000, $1,100 and $1,200 on items, the unit cost of which were $5.00, $6.25, $5.50 and $6.00 respectively.To the nearest cent, the mean price paid per item was ( )
- A company has decided to lease a machine. Six annual payments of $8,000 will be made with the first payment on receipt of the machine. Below is an extract from an annuity table:
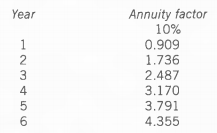
What is the present value of the lease payments at an interest rate of 10%? ( ) - Which of the following statements is correct?( )
- Which of the following best describes management by exception?( )
- Which method of investment appraisal leads to the selection of projects that maximise shareholder wealth? ( )
- The following statements relate to spreadsheets. Which statement is false? ( )
- Which of the following are benefits of using activity based costing? ( )(i) It recognises that overhead costs are not always driven by the volume of production(ii) It does not result in under or over absorption of foxed overheads(iii) It avoids all arbitrary cost apportionments(iv) It is particularly useful in single product businesses
- An investment project has net present values as follows.At a discount rate of 5% $69,700 positive At a discount rate of 14% $16,000 positive At a discount rate of 20% $10,500 negative Using the above figures what is the best approximation of the internal rate of return of the investment project? ( )
- 20,000 litres of liquid were put into a process at the beginning of the month at a cost of $4,400. The output of finished product was 17,000 litres. The normal level of waste in this process is 20% and the waste which is identified at the end of the process can be sold at $0.50 per litre. What is the abnormal gain or loss and what is the cost per unit? ( )
- A company is considering accepting a one-year contract which will require four skilled employees. The four skilled employees could be recruited on a one-year contract at a cost of $40,000 per employee. The employees would be supervised by an existing manager who earns $60,000 per year. It is expected that supervision of the contract would take 10% of the manager's time. Instead of recruiting new employees the company could retrain some existing employees who currently earn $30,000 per year. The training would cost $15,000 in total. If these employees were used they would need to be replaced at a total cost of $100,000. What is the relevant labour cost of the contract? ( )
- The following information is available for the month of June. Budgeted hours 2,850 standard hours Standard hours produced 3,150 standard hours Actual hours worked 3,000 The following information is available for the month of July. Budgeted hours 2,750 standard hours Standard hours produced 2,800 standard hours Actual hours worked 3,000 Calculate the percentage change in the activity ratio from June to July. Work to the nearest whole percentage. ( )
- What is goal congruence (in terms of organisational control systems)? ( )
- Jane works as a member of a three-person team in the assembly department of a factory.The team is rewarded by a group bonus scheme whereby the team leader receives 40 per cent of any bonus earned by the team, and the remaining bonus is shared evenly between Jane and the other team member.Details of output for one day are given below.Hours worked by team 8 hoursTeam production achieved 80 unitsStandard time allowed to produce one unit 9 minutesGroup bonus payable at $6 per hour 70% of time savedWhat is the bonus element of Jane's pay for this particular day? ( )
- A company uses production labour hours to absorb its fixed production overheads. A strike by its workforce results in a loss of 30% of the period's budgeted production labour hours. Which of the following variances will occur as a result of the loss in production labour hours? ( )
- The arithmetic mean of nineteen numbers is 10. When a twentieth number, x, is added the overall mean becomes 11 . What is the value of x? ( )
- The overhead absorption rate for product Y is $2.50 per direct labour hour. Each unit of Y requires 3 direct labour hours. Inventory of product Y at the beginning of the month was 200 units and at the end of the month was 250 units. What is the difference in the profits reported for the month using absorption costing compared with marginal costing? ( )
- In a period, a company had opening inventory of 31,000 units and closing inventory of34,000 units. Profits based on marginal costing were $850,500 and on absorption costing were$955,500.If the budgeted total fixed costs for the company was $1,837,500, what was the budgeted levelOf activity in units? ( )
- Which of the following would be the most appropriate basis for apportioning machinery insurance costs to cost centres within a factory? ( )
- A firm with current assets of $40 million and current liabilities of $20 million buys $5 million of inventory on credit which increases its inventory level to $10 million. What will the effect be on its current ratio and quick (acid test) ratio?( )
- What is a by- product? ( )
- X Co has recorded the following wages costs for direct production workers for November. ( ) $Basic pay 70,800Overtime premium 2,000Holiday pay 500Gross wages incurred 73,300The overtime was not worked for any specific job.What are the accounting entries for these wages costs?
- Over- absorbed overheads occur when( )
- Overheads in a factory are apportioned to four production cost centres (A, B, C and D). Direct labour hours are used to absorb overheads in A and 巳 and machine hours are used in C and D. The following information is available:

Which cost centre has the highest hourly overhead absorption rate? ( ) - Which of the following would be suitable for measuring resource utilisation in a parcel delivery company?( )
- Which of the following best describes the advantage of a balanced scorecard approach?( )
- Which of the following statements are true?(i) The fixed overhead volume capacity variance represents part of the over/under absorption of overheads(ii) A company works fewer hours than budgeted. This will result in an adverse fixed overhead volume capacity variance
- Which of the following would be classed as indirect labor? ( )
- A company sold 56,000 units of its single product in a period for a total revenue of $700,000. Finished inventory increased by 4,000 units in the period. Costs in the period were :Variable production $3.60 per unitFixed production $258,000 (absorbed on the actual number of units produced)Fixed non- production $144,000Using absorption costing, what was the profit for the period? ( )
- Which of the following statements are true? (i) An investment with a positive NPV is viable.(ii) IRR is technically superior to NPV.(iii) Both IRR and NPV give the same accept or reject decision, regardless of the pattern of thecash flows.
- Which of the following situations is most likely to result in a favourable selling price variance?( )
- The balanced scorecard measures performance from four perspectives. What are they? ( )
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of quota sampling? ( )
- Harry P Co uses 62,500 units of material HP at an even rate during the year. Each order placed with the supplier of the units is for 5,000 units, which is the EOQ. The company holds buffer inventory of 1,250 units. The annual cost of holding one unit in inventory is $5. What is the total annual cost of holding inventory of the unit? ( )
- Build Co is a company that constructs office buildings and has decided that it will build its new head office. Which of the following costs should be included in the recorded cost of the new building? (i) Raw materials(ii) Labour costs(iii) Related overhead costs(iv) Legal costs that will be incurred to purchase the land
- A company has over- absorbed fixed production overheads for the period by $6,000. The fixed production overhead absorption rate was $8 per unit and is based on the normal level of activity of 5,000 units. Actual production was 4,500 units. What was the actual fixed production overheads incurred for the period?
- The following information relates to a company's polishing process for the previousperiod.Output to finished goods 5,408 units valued at $29,744Normal loss 276 unitsActual loss 112 unitsAll losses have a scrap value of $2.50 per unit and there was no opening or closing work inprogress.What was the value of the input during the period? ( )
- A chemical is manufactured in two processes, X and Y. Data for process Y for last month are as follows.Material transferred from process X 2,000 litres @ $4 per litreConversion costs incurred $12,240Output transferred to finished goods 1,600 litres No losses occur in the process. Closing work in progress is fully complete for material, but is only 50% processed. What is the value of the closing work in progress (to the nearest $)? ( )
- Which one of the following statements does NOT explain why coding systems are used? ( )
- In a period 12,250 units were made and there was a favourable labour efficiency variance of $11,250. If 41,000 labour hours were worked and the standard wage rate was $6 per hour, how many standard hours (to two decimal places) were allowed per unit? ( )
- A company made 17,500 units at a total cost of $16 each. Three quarters of the costs were variable and one quarter fixed. 15,000 units were sold at $25 each. There were no opening inventories. By how much will the profit calculated using absorption costing principles differ from the profit if marginal costing principles had been used? ( )
- A company budgeted to sell 5,000 units of a product in November at a standard price of $30 per unit and to earn a profit of $25,000. It actually sold 6,000 units at $28 per unit and earned a profit of $32,000. What was the favourable sales volume profit variance for November? ( )
- Which of the following would be data rather than information?
- The following scores are observed for the times taken to complete a task, in minutes.24, 68,28,30,42,48, 18,34,22, 16 The median score is ( )
- A cost which contains both fixed and variable elements, and so is partly affected by changes in the level of activity, is called: ( )
A: (ii) only B:(i), (ii) and (iii) only C:(i) only D:(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
答案:(i), (ii) and (iii) only
A:A selling and distribution overhead
B:A direct production expense
C:A production overhead
D:A part of prime cost
答案:A: A selling and distribution overhead
A:Item (ii) only
答案:Items (ii) and (iii) only
A:5.13%
答案:0.26%
A:None
答案:None
A:Re-inspection cost
B:Performance testing
C:Administration of customer complaints section
D:Training in quality control
答案:Performance testing
A:$5.69
B:$5.72
C:$5.70
D:$5.71
答案:$5.69
A:$34,840
B:$48,000
C:$38,328
D:$30,328
答案:$38,328
A:The operating standards set for production should be the attainable level
B:The operating standards set for production should be the minimal level
C:The operating standards set for production should be the maximum level
D:The operating standards set for production should be the most ideal possible
答案:The operating standards set for production should be the attainable level
A:Sending management reports only to those managers who are able to act on the information contained within the reports
B:Focusing management reports on areas which require attention and ignoring those which appear to be performing within acceptable limits
C:Using management reports to highlight exceptionally good performance, so that favourable results can be built upon to improve future outcomes
D:Focusing management reports on areas which are performing just outside acceptable limits
A:Net present value
B:Internal rate of return
C:Wealth rate of return
D:Discounted payback
A:They allow data to be displayed graphically
B:They allow the font, size and colour of text to be changed
C:They are an efficient method of storing text based files
D:They facilitate 'what if analysis
A:(i) and (ii) only B: (i) and (iv) only C: (i) only D:(ii) and (iii) only
A:17.9%
B:18.0%
C:22.7%
D:17.6%
A:Abnormal gain $1,000, cost per unit $0.28
B:Abnormal loss $1,000, cost per unit $0.15
C:Abnormal loss $1,000, cost per unit $0.28
D:Abnormal gain $1,000, cost per unit $0.15
A:$275,000
B:$160,000
C:$115,000
D:$135,000
A:8%
B:109%
C:9%
D:92%
A:When the work-related goals of management harmonise with their personal goals
B:When an organisation's goals harmonise with those of its customers
C:When the goals of management and employees harmonise with the goals of the organisation as a whole
D:When the goals of management harmonise with the goals of employees
A:$10.08 B:$16.80 C:$7.20 D:$5.04
A:Adverse direct labour efficiency variance
B:Adverse fixed overhead efficiency variance
C:Adverse fixed overhead capacity variance
D:Adverse direct labour rate variance
A:20
B:15
C:25
D:30
A:The absorption costing profit would be $375 greater.
B:The absorption costing profit would be $375 less.
C:The absorption costing profit would be $1,875 greater.
D:The absorption costing profit would be $125 greater.
A:32,500
B:52,500
C:65,000
D:105,000
A:The number of machines in each cost centre
B:The operating hours of the machinery in each cost centre
C:The value of the machinery in each cost centre
D:The floor area occupied by the machinery in each cost centre
A:Current ratio Increase by 25% Liquidity ratio Reduce by 20% B:Current ratio Reduce by 10% Liquidity ratio Reduce by 20% C:Current ratio Reduce by 10% Liquidity ratio Unchanged
A:A product produced at the same time as other products which has no value
B:A product produced at the same time as other products which requires further processing to put it in a saleable state
C:A product produced at the same time as other products which has a relatively low value compared with the other products
D:A product produced at the same time as other products which has a relatively low volume compared with the other products
A: Debit Credit
$ $
Wages control account 73,300
Work in progress account 72,800
Overhead control account 500
B: Debit Credit$ $
Work in progress account 72,800
Overhead control account 500
Wages control account 73,300
$ $
Wages control account 73,300
Work in progress account 70,800
Overhead control account 2,500
$ $
Work in progress account 70,800
Overhead control account 2,500
Wages control account 73,300
A:Absorbed overheads exceed actual overheads B:Actual overheads exceed absorbed overheads C:Absorbed overheads exceed budgeted overheads
A:Production Cost Centre A
B:Production Cost Centre B
C:Production Cost Centre C
D:Production Cost Centre D
A:Cost per consignment
B:Client evaluation interview
C:Depot profit league tables
D:Number of customer complaints
A:The balanced scorecard approach enables organisations to consider all areas of performance relevant to achieving their strategic goals
B:The balanced scorecard approach enables organisations to demonstrate their ethical credentials
C:The balanced scorecard approach enables organisations that are struggling financially to emphasise other areas
D:The balanced scorecard approach enables organisations to more easily benchmark their performance against others
A:(i)is false and (ii) is false B:(i)is true and(ii) is false C:(i)is false and (ii) is true
A:A consultant in a firm of management consultants B:Assembly workers in a company manufacturing televisions C:A store assistant in a factory store D:Plasterers in a construction company
A:$82,000
B:$123,200
C:$113,600
D:$96,400
A:(i), (ii) and (iii) B:(i) and (ii) only C:(i) only D:(i) and (iii) only
A:Demand for the product was higher than expected and prices could be raised without adverse effects on sales volumes.
B:Competitors charged lower prices than expected, therefore selling prices had to be reduced in order to compete effectively.
C:Fewer customers than expected took advantage of the early payment discounts offered.
D:The sales director decided to change from the planned policy of market skimming pricing to one of market penetration pricing.
A:Customer satisfaction, growth, financial success and process efficiency
B:Customer satisfaction, growth, financial stability and process efficiency
C:Customer retention, growth, financial stability and process efficiency
D:Customer satisfaction, growth, financial success and process effectiveness
A:It is expensive.
B:It is administratively complicated.
C:A sampling frame is necessary.
D:It can result in certain biases.
A:$18,750
B:$12,500
C:$15,625
D:$25,000
A:All of them
A:$40,000 B:$36,000 C:$42,000 D:$30,000
A:$29,532
B:$29,744
C:$28,842
D:$30,434
A:$1,360
B:$2,960
C:$2,160
D:$4,320
A:A code is more precise than a description so reduces ambiguity
B:A code is more suited to communicating wider issues than a description
C:The use of codes facilitates data processing
D:A code is briefer than a description so saves time
A:5
B:4
C:4.5
D:3.5
A:The absorption costing profit would be $10,000 greater
B:The absorption costing profit would be $30,000 greater
C:The absorption costing profit would be $40,000 greater
D:The absorption costing profit would be $10,000 less
A:$5,000
B:$12,000
C:$30,000
D:$7,000
A:Sales increase/ decrease per product in last quarter
A:32
B:29
C:28
D:26
A:A direct cost
B:A semi-variable cost
C:An unavoidable cost
D:A prime cost

