- Which are the main stages of listening teaching? ( )
- Which are from social-constructivist theory? ( )
- Which generally should be pronounced as strong form while reading aloud? ( )
- Which of the following activities can be practiced with listening? ( )
- Which of the following activities are often used to develop students’ speaking fluency? ( )
- Please find out which activities can be used in class to cultivate learner’s visual literacy? ( )
- Factors influencing pronunciation study are: ( )
- What should teachers do to help learners in discourse competence cultivation? ( )
- Teachers as guides means ( ).
- To teach pronunciation effectively, you need several types of knowledge: ( )
- WHERETO teaching design principle refers to ( )
- Which of the following statements are the characteristics of speaking process? ( )
- How to make effective classroom instructions? ( )
- What are the characteristics of classroom instruction? ( )
- Which of the following are not controlled activities in an English class? ( )
- The success of classroom learning is very much dependent on ( )
- Which are the descriptions of cognitive theory? ( )
- The teaching design cares about what the learners have learnt and how they learnt it. ( )
- Setting the scene in teaching listening aims to activate students’ schema and make them better prepared to understand what they hear. ( )
- Teachers sometimes assume that shyer students will be able to learn pronunciation better than the more outgoing learners. ( )
- Topdown processing expects the listener to have a very effective shortterm memory as they have to make sense of every sound in order to figure out the meaning of words, phrases, and structure. ( )
- In foreign language learning, both listening and reading are receptive skills, but listening can be more difficult than reading. ( )
- In the Top-down Model, not only linguistic knowledge but also background knowledge is involved in reading. ( )
- Methods and quality of pronunciation teaching won’t influence students’ pronunciation study. ( )
- Grammar teaching is less important in writing than in listening and reading. ( )
- Using stress, rhythm, and intonation to express meaning is cultivating learner’s linguistic competence. ( )
- The way to acquire the sentence patterns of the target language is repetition of dialogues about everyday situations. ( )
- “See a movie” and “watch a play” both are collocations. ( )
- Confident students might speak more and be more willing to try new sounds, and this extra practice could help them improve their pronunciation. ( )
- People can remember the exact form of the message they hear, that is they remember what they hear word for word. ( )
- No teacher can force students to learn well if they’re not motivated. ( )
- Which of the following instruction is helpful in developing students’ ability to make inference? ( )
- It is suggested that teachers should not interrupt students for error correction when the activity aims at _______. ( )
- For WHERETO teaching design principle, T refers to ( ).
- When students do skimming and scanning tasks, it is very important for the teacher to control time. What role does the teacher play? ( )
- Strategic competence concerned with ( ).
- Which of the following shows the correct sentence stress in normal cases? ( )
- In speaking class, the teacher uses phrases such as “Wow” “My goodness” “Pardon” to communicate with students. Which principle does this teacher focus on? ( )
- As a 21st century teacher, which opinion on integrating technology into class is right? ( )
- In a listening class, a teacher asks students to listen to the material carefully and try to discriminate the speaker’s attitude towards lifelong learning. What sub-skill of listening is the teacher training? ( )
- There are some speaking activities. Which of the following mainly focus on the form and accuracy? ( )
- When organizing feedback, it is very discouraging for the teacher to be ( ).
- Which one you cannot refer to for your self-directed learning? ( )
- Learning is a process in which the learner constructs meaning based on his/her own experiences and what he/she already knows. This description belongs to ( ).
- Before students start the activity, the teacher should give instruction clearly and concisely so that students know how to do what. What role does the teacher play? ( )
- The synonyms “charge” and “accuse” mainly differ in ______. ( )
- approach means teacher and learners collaborate on and co-construct the grammar explanation. ( )
- Gentle correcting involves showing that incorrectness has occurred, but not making a big fuss about it. What role does the teacher play? ( )
- What does the critical mean in three-dimension paradigm? ( )
- Research shows that there are a wide range of benefits derived from improved visual literacy including: ( )
- What kind of speaking activities are more communicative? ( )
- The traditional grammarians classify grammar into and , so the close relationship between grammar and vocabulary, grammar and sentences exists. ( )
- ADDIE model includes ( ).
- Which are while-listening activities? ( )
- Why do students need to predict before reading? ( )
- Which are the ways of consolidating vocabulary? ( )
- What will also help children know which letters to use when they are reading words? ( )
- What are the components of communicative competence? ( )
- Which activities are appropriate in the post-listening stage? ( )
- What are the possible reasons for students’ poor listening skill? ( )
- Non-native language listeners can automatically use two processes (bottom-up processing and top-down processing) interactively. ( )
- Labelling means that students construct the series following an example. ( )
- Note-taking and gap-filling is a good example of how while-listening and post-listening is combined. ( )
- Good teachers constantly reflect on what they do as a teacher keen on improving their teaching and their students’ learning on the basis of researching the classroom. ( )
- Grading difficulty level appropriately is one principle for teaching listening. ( )
- The influence of the learner’s language is one of the influencing factors of pronunciation study. ( )
- Organizing feedback is not an effective way to assess students’ performance so that they see the extent of their success or failure. ( )
- Creating and evaluating belong to the higher order thinking ability. ( )
- Images can greatly enrich the students’ understanding of a text or other media, but to be able to interact with these deeper levels of meaning, students must possess the necessary skills to access those depths. ( )
- The denotative meaning of a dog means being loyal and friendly. ( )
- Research has shown that children who have not developed reading skills by first grade, will experience an overall delay in learning throughout their school life. ( )
- When designing listening tasks, it is not necessary to grade the difficulty level of the tasks. ( )
- According to the Interactive Model of reading, reading is based on the theory in which reading (and listening, too) is regarded as a process of “decoding”, which moves from the bottom to the top of the system of language. ( )
- Which of the following is not the principle for teaching speaking? ( )
- For cognitive level of creating, the teacher may ask students the question like ( ).
- When a teacher creates a real life situation for his students to discuss, he expects them not to focus on ____ too much. ( )
- When a teacher tells students that the word “dog” may imply “loyalty”, he/she is teaching the _____ of the word. ( )
- What does Top-down model mean? ( )
- approach means teachers provide explanation on grammatical rules for learners. ( )
- ZPD means: ( )
- What type of approach does the student apply to listening according to what he describes? “When I listen to English tapes, I am always worried about my limited vocabulary. I tend to figure out its actual meaning when coming across an unknown word, so that stop makes me mist the next part of the speech.” ( )
- The relationship between “furniture” and “desk” is ______. ( )
- a model for contextualizing lessons with learners about language form in the context of interesting cultural texts. ( )
- Which of the following assumptions fails to describe the nature of vocabulary or vocabulary learning? ( )
- What are the two major purposes in listening? ( )
- On what aspects can the PACE model help develop? ( )
- Which of the following activities belong to meaningful practice? ( )
- What are the views of language learning? ( )
- What purpose do post-listening activities serve? ( )
- Teachers as researchers means ( ).
- What are the three-dimension paradigm by Callow (2005)? ( )
- Which are involved in bottom-up processing while listening? ( )
- What do the two aspect of vocabulary learning involve according to Hedge (2000)? ( )
- Which are principles for teaching speaking? ( )
- Which activities are while-listening activities? ( )
- The basic principles of teaching pronunciation are: ( )
- Written language can be compared to a code, so knowing the sounds of individual letters and how those letters sound when they’re combined will help children words as they . ( )
- Which of the following activities are communicative ones in teaching speaking? ( )
- Which of the following activities are ways of consolidating vocabulary? ( )
- Training is a controlled practice after the presentation of linguistic items. This practice is strictly controlled by a teaching and usually takes the form of pattern drills. Which of the following drills are usually included? ( )
- The first step of PACE represents the “whole” language being presented in a thematic way. It can be , , , and , etc. ( )
- What should teachers do to help learners in strategic competence cultivation? ( )
- Which of the following activities are visual or physical demonstrations? ( )
- Which practices are structure-based with a focus on forms? ( )
- What is the significance for the variety of English-speaking activities? ( )
- Which are the descriptions of behaviorist theory? ( )
- Listening is not an isolated skill and should be developed together with other skills. ( )
- For constructivist theory, teachers need to design environments and interact with learners to foster inventive, creative, critical learners. ( )
- Children can learn the sounds of language more naturally than adults and can approach native speaker pronunciation at all events. ( )
- It is believed that the more communicative an activity is, the less control it needs. ( )
- Before students start the activity, the teacher should give instruction clearly and concisely so that students know how to do what. ( )
- Doing information-gap activities is an excellent way to make speaking tasks more communicative. ( )
- Students’ pronunciation learning is affected by how much English they have a chance to hear in their daily lives. ( )
- Accuracy-based practices are more important than fluency-based practices. ( )
- Having students listen to a recording to the teacher’s voice and then repeat is a useful and enough part of a pronunciation lesson. ( )
- Hyponyms refer to words which can be grouped together under the same superordinate concept. ( )
- In phonics, after kids know the sound of each letter makes, teachers can combine some letters together to let students read them out. ( )
- Before organizing an activity in the class, the teacher anticipate problems that may arise when the activity is being carried out. ( )
- Chunks refer to a group of words what go together to form meaning. ( )
- The new curriculum stipulates that the teacher should function as a facilitator to students’ learning rather than simply transmitting knowledge. ( )
- An appropriate degree of control of the teacher over the class is not vital in formal language teaching. ( )
- The activity must create a desire to communicate among the students. That is, even if communication is forced on the students, they must feel a real need to communicate. ( )
- A learner’s first language has a weak influence on the way he or she learns the pronunciation of a second language. ( )
- Giving students feedback throughout the composing process (not just on the final product) to consider as they attempt to bring their expression closer and closer to intention is one of the features of product-oriented approach of writing teaching. ( )
- Productive/active vocabulary refers to an individual’s vocabulary that he or she regularly uses. ( )
- Teaching phonics with games could help students link the sounds together to bring out a word. ( )
- Helping them build repertoires of strategies for prewriting, drafting, and rewriting is one of the features of product-oriented approach of writing teaching. ( )
- To perform functions, learners need to know how to combine the grammatical rules and the vocabulary to express notions that perform the functions. ( )
- Bottom-up Model of teaching reading is based on the theory in which reading (and listening, too) is regarded as a process of “decoding”, which moves from the bottom to the top of the system of language. ( )
- A teacher may encourage students to ____ when they come across new words in fast reading. ( )
- Which of the following shows the general intonation pattern of a coordinate sentence? ( )
- When students learn “apple, orange”, the teacher gives students another word “fruit”. Which principle does the teacher follow in his/her vocabulary teaching? ( )
- Which of the following shows the general intonation pattern in a complex sentence? ( )
- Which is not the reading teaching principle? ( )
- Which is not the best way to explain the new words to learners? ( )
- If a teacher attempts to implement the bottom-up model to teach listening, he/she is likely to present ______. ( )
- A dialogic approach embedded in the use of meaningful contexts found in compelling and interesting stories might hold the key to dramatic improvements in the acquisition of . ( )
- Which is not the description of behaviorist theory? ( )
- Which of the following is a plosive? ( )
- Which of the following activities is not communicative activity in teaching speaking? ( )
- What question does not belong to “the critical” part in three-dimension paradigm? ( )
- The difference between /ʃ/ and /ʒ/ lies in . ( )
- In the following activities, which one needs most control? ( )
- The similarity between the English consonants /p/, /b/ and /m/ is that they are all . ( )
- Scaffolding excludes: ( )
- Fluency concerned with ( ).
- Which is not the feature that teachers have in their survival stage? ( )
- When the teacher attempts to elicit more information from the students by saying “And …?” “Good. Anything else?”, etc., he/she is playing the role of a _____. ( )
- In a listening class, the teacher asks students to role-play the dialogue according to the listening material. Which stage does this activity belong to? ( )
- For new language learning, the aspect that students do not need to do with is ( )
- approach means learners analyze the grammar explanation for themselves. ( )
- What are the benefits that the technology integrated into the language class? ( )
- Please choose the technology that can be integrated into the language class. ( )
- Which online technologies cannot be used for improving writing teaching?
- Many young students have grown up with 21st-century digital technology; it is just part of their normal world. They are called as ( ).
- Making a show with pictures on which words and explanations are listed by some software cannot assist your vocabulary teaching. ( )
- As a 21st century teacher, which opinion is not right? ( )
- The 21-st century teacher needs to take the time to be comfortable with those technological tools that are useful for their students. ( )
- As we become more familiar and more comfortable with our technology tools, we need to start finding ways to elegantly integrate them into our normal teaching. ( )
- New technology provides a wide range of ways for us to help learners improve their skills. ( )
- Which can be used to teach listening and speaking? ( )
- In order to offer assistance to teachers in the Survival stage, it is important to provide off-site guidance for specific teaching skills and suggestions to meet group and individual needs of students. ( )
- What are the features that teachers have in their survival stage? ( )
- A change from a suburban to an urban setting may also result in an experienced teacher moving to a lower stage of development, and as such, they may need assistance with strategies that will help them become successful in this new context. ( )
- Who are often interested in professional development opportunities that are available through local, state, or national organizations? ( )
- In the survival stage, teachers are focused on themselves and their own needs and also have much understanding of their students and their needs. ( )
- Which stage do teachers begin to ask questions of themselves and their teaching that focus on insights, perspectives, and beliefs of teaching and children? ( )
- to participate in conferences and seminars and to accept leadership positions in their school, community, or professional organization. ( )
- Which is not the developmental stage for in-service teachers? ( )
- In the maturity stage, what questions do teachers may ask? ( )
- Which are the developmental stages for in-service teachers? ( )
- Which will not help teachers motivate students to write? ( )
- What are the features for process-oriented writing teaching? ( )
- Which principles will motivate students to write? ( )
- Simply giving students a topic and asking them to write on their own will not make them frustrated because many of them know where to start and how to develop ideas. ( )
- Which principles can help teachers motivate students to write? ( )
- Enabling students to experience a sense of achievement from time to time is quite crucial in motivating students to continue practicing writing. ( )
- What does process approach to writing mean? ( )
- Prewriting activities, like brainstorming or a class discussion on the topic will help students broaden their views and encourage a generation of ideas. ( )
- What product-oriented method of teaching writing mean? ( )
- If the topic is too far away from students' life, they will have difficulty finding content to write, as a result, they will be demotivated. ( )
- According to the Interactive Model of reading, when one is reading, the brain receives visual information, and at the same time, interprets or reconstructs the meaning that the writer had in mind when he wrote the text. ( )
- What are the principles for reading teaching? ( )
- In the Top-down Model, the teacher teaches reading by introducing vocabulary and new words first and then going over the text sentence by sentence. ( )
- Which is not the reading skill that the learners should be developed in reading class? ( )
- As with everything else in lessons, students who are not engaged with the reading text will not actively interested in what they are doing. ( )
- What does bottom-up model mean? ( )
- Find out the reading skills that the learners should be cultivated in reading class. ( )
- When expectations are set up, what kind of process of reading is ready to begin? ( )
- Reading comprehension involves extracting the relevant information from the text as efficiently as possible, connecting the information from the written message with one’s own knowledge to arrive at an understanding. ( )
- What are the models for reading teaching? ( )
- Information presented visually is processed extremely quickly by the brain. ( )
- Which is not the teaching step of viewing teaching? ( )
- What are the pedagogical questions that the teacher can use in class to develop learners’ visual literacy? ( )
- As these students travel on their road to fluency in English, images can provide an effective bridge in that learning process. ( )
- Which are the teaching steps of viewing teaching? ( )
- One of the most effective ways to encourage information to make that important jump from the limited short-term memory to the more powerful long-term memory is to pair text with images. ( )
- What is the definition of Visual literacy? ( )
- We need to consider the active viewer as well and engage the students' creative or curative responses to the image. ( )
- Which is not the three-dimension paradigm by Serafini (2014)? ( )
- What can be used as visual literacy clues to facilitate identifying the visual products? ( )
- Which belong to common features of spoken language according to Bygate (1987)? ( )
- Which is not the principle for teaching speaking? ( )
- Designing speaking activities that maximize students’ opportunity to speak is one of the central tasks for language teachers. ( )
- Like all the other skills, what strategies does speaking involve?( )
- Problem-solving activities tend to be productive because there is a clear objective to be reached or problem to be solved and require a higher level of language proficiency. ( )
- Speaking is the skill that the students will be judged upon most in simulated situations. ( )
- Which of the following activities is often used to develop students’ speaking accuracy? ( )
- Maintaining a balance between accuracy-based and fluency-based practices is essential in teaching speaking.( )
- Which practice is not structure-based with a focus on forms? ( )
- Which belong to typical speaking tasks? ( )
- What are three main categories that affect the difficulty level of listening tasks according to Anderson and lynch (1988)? ( )
- In the top-down model, listening for gist and making use of the contextual clues and background knowledge to construct meaning are emphasized. ( )
- Which belong to principles for teaching listening? ( )
- Multiple-choice tests play a decisive role in helping students develop good listening habits and strategies. ( )
- What are two models that are frequently used to describe different processes of listening? ( )
- Which is not the main listening difficulty of learners? ( )
- Which is not the stage of listening teaching? ( )
- Which is not involved in bottom-up processing while listening? ( )
- It is important to develop listening skills together with other skills because ordinarily listening is not an isolated skill. ( )
- Bottom-up and top-down these two processes are mutually dependent. ( )
- That the students are asked to produce language based on pictures and key phrases provided by the teacher is using chained phrases for storytelling. ( )
- is an approach that removes you, the teacher, from the main role of “explainer” and extends to the students the opportunity to question and discover the target grammar. ( )
- Using prompts has proved to be an effective way of grammar practice. The prompts can be: ( )
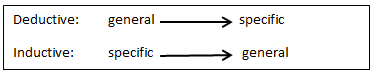
- Deductive reasoning is essentially a approach which moves from the more general to the more specific. ( )
- Although inductive teaching takes longer than deductive, many educators agree it is a very efficient method in the long run. Benefits include: ( )
- Although a little less effective than inductive teaching, benefits to the deductive approach are: ( )
- usually comes after mechanical practice. ( )
- Grammar practice is usually divided into two categories, mechanical practice and meaningful practice. ( )
- In mechanical practice the focus is on the production, comprehension or exchange of meaning through the students “keep an eye on” the way newly learned structures are used in the process. ( )
- Which belong to vocabulary learning strategies? ( )
- Antonyms refer to the sameness or close similarity of meaning or we can say that words are close in meaning. ( )
- Collocations refer to words that co-occur with high frequency and have been accepted as ways for the use of words. ( )
- Receptive/passive vocabulary refers to words that one is able to recognize and comprehend in reading or listening but unable to use automatically in speaking or writing. ( )
- Denotative meaning refers to those words that we use to label things as regards real objects, such as a name or a sign, etc. in the physical world. ( )
- What does knowing a word involve? ( )
- According to Hedge (2000), what does the second aspect of vocabulary learning involve? ( )
- Which is not a collocation? ( )
- Which is not the appropriate way of consolidating vocabulary? ( )
- What does the first aspect of vocabulary learning involve according to Hedge (2000)? ( )
- A lot of people start the journey of teaching kids phonics through the traditional ways, like teaching them to read, and this is the best way to follow. ( )
- Understanding phonics will also help children know which letters to use when they are writing words. ( )
- Phonics is a method for teaching and of the English language by developing learners' phonemic awareness—the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate phonemes—in order to teach the correspondence between these sounds and the spelling patterns that represent them. ( )
- Which generally should be pronounced as weak form while reading aloud? ( )
- What is the best age to start learning to read through phonics? ( )
- Sound /k/ can be spelled as ? ( )
- Research has shown that children who have not developed reading skills by second grade, will experience an overall delay in learning throughout their school life. ( )
- Written language can be compared to a code, so knowing the sounds of individual letters and how those letters sound when they’re combined will help children code words as they read. ( )
- After learning the individual letters’ sounds, it is natural to learn the sounds of ? ( )
- What is used to express meanings in many subtle ways such as surprise, complaint, sarcasm, delighted, threats, etc.? ( )
- What are the frequently applied teaching models? ( )
- What does WHERETO teaching design principle refer? ( )
- The purpose of teaching design is to implement teaching effectively. ( )
- Activation of prior knowledge means activating cognitive structures that relate to the topics and tasks to be studied and completed. ( )
- Which belongs to teaching design principle? ( )
- For WHERETO teaching design principle, R refers to ( ).
- For WHERETO teaching design principle, W refers to ( ).
- SMART is the method for articulating learning objectives. ( )
- Develop student’s reading skills. This learning objective is appropriately presented. ( )
- What are the four elements of articulating learning objectives? ( )
- Which belong to teacher’s role? ( )
- For cognitive level of analyzing, the teacher may ask students the question like ( ).
- For cognitive level of evaluating, the teacher may ask students the question like ( ).
- Which one does not belong to the Bloom’s Taxonomy (2001)? ( )
- Teacher Talk Time means teacher should talk more in class and do not leave silence gap in class. ( )
- Allow learners in class the time and the quiet they need, because they need time to think, to prepare what they are going to say and how they are going to say it. ( )
- Even the clearest instructions can be hard to grasp so, after you've given them, it's worth checking that they have been understood. ( )
- Remembering and understanding belong to the higher order thinking ability. ( )
- What are the two things that the teacher does as an assessor? ( )
- Teachers as facilitators means ( ).
- Which aspects belong to communicative activity? ( )
- Which aspects do not belong to communicative activity? ( )
- The communicative activity must involve the students in performing a real communicative purpose rather than just practicing language for its own sake. ( )
- Discourse competence concerned with ( ).
- What should teachers do to help learners in linguistic competence cultivation. ( )
- Mother tongue is encouraged in the classroom by audiolingual method. ( )
- Communicative purpose means ( ).
- What are the four teaching procedures of audiolingual method? ( )
- What should teachers do to help learners in linguistic competence cultivation? ( )
- The Audiolingual Method is a method of foreign language teaching which emphasizes the teaching of reading and writing before listening and speaking. ( )
- The functional view only sees language as a means for doing things. ( )
- The structural view of language is that language is a system of structurally related elements for the transmission of meaning. ( )
- Which belong to condition-oriented theory? ( )
- Which is not the view of language Learning? ( )
- Which is not the view of language? ( )
- For new language learning, the aspects that students need to do with are ( )
- Which belong to process-oriented theory? ( )
- Which is from social-constructivist theory?
- Learning should be achieved via the dynamic interaction between the teacher and the learner and between learners. ( )
- For behaviorist theory, mistakes should be immediately corrected, and the correction should be immediately praised. ( )
- 英语学科教学论,是一门介绍如何教英语的课。
- 关于教英语,还需要了解相关的教学方法、了解课堂管理的内容、学习教学设计的理念等。
- 听说读写看的教学,是关于语言技能的教学。
- 关于教英语,需要了解相关的语言和语言学习的理论。
- 英语学科教学论,是介绍英语知识的一门课。
答案:While-listening.###Post-listening.###Pre-listening.
答案:ZPD###Scaffolding
答案:Verb.###Adjective.###Noun.
答案:Retelling.###Note-taking.###Writing task.###Role-plays.
答案:Describing people in pair.###Acting out the dialogue in the text.###Having discussions in groups.
答案:Rewrite the accompanying text or script as if it were a different genre. What changes take place?###Embed the image in a different context or genre.###Identify the subtext of a particular image or video sequence and present this to others.###Research and find similar images or videos online.
答案:motivation###personality and attitude###exposure to the language###critical period for language acquisition
答案:understand and use emotive tone###select language forms appropriate to topic, listener, or setting
答案:to give them equal opportunities in learning###to active students’ prior knowledge###to find each student’s interests and explore their potential capabilities
答案:You need to understand and be able to predict the kinds of problems your students might have with pronunciation and why they happen.###You need to know the facts about pronunciation###You need to know many ways to teach pronunciation to your students.
答案:help the students know where the unit is going and what is expected###allow students to evaluate their work and its implication’s###equip students, help them experience the key ideas and explore the issues
温馨提示支付 ¥5.00 元后可查看付费内容,请先翻页预览!

