1.已知不可压缩流体作平面定常流动,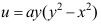 ,当
,当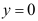 时,
时,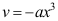 ,则
,则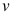 =( )。
=( )。
A:
B:
C:
D:
答案:AI参考:正确答案是:B: \n流量恒定不变,流体是不可压缩的,故其密度ρ也是恒定的。对于定常流动,压强与流速的平方成正比,因此,当流量不变时,压强与流速成反比。由题可知,流体从A到B流速增大,压强减小,故A错误;流体从B到C流速减小,压强增大,故B正确;而流体从A到C的流量不变,故C错误;D项无法从题中得出。故本题答案为B。'
2.圆管层流过流断面上的流速最大值位于管轴处,切应力最大值位于( )处。
A:管轴
B:壁面
答案:AI参考:正确答案是B:壁面。\n流体在壁面处受到管道壁面的摩擦阻力最小,流速最大,所以壁面处流速最大;而切应力在流体的粘性内摩擦力作用下产生,因此切应力最大值位于壁面处。因此,选项B是正确答案。'
3.已知流动的速度分布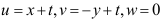 。则流线为( )。
。则流线为( )。
A:
B:
C:
D:
答案:AI参考:正确答案是D:流线是表示流体运动中各点速度矢量相等的曲线。\n根据题干中给出的流动速度分布图,可以发现流线上的各点速度大小相等,方向相同,因此流线表示的是流体运动中各点速度矢量相等的曲线,故选D。'
4.不可压缩粘性流体在水平圆管中的压力损失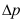 与管内径
与管内径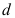 、管壁绝对粗糙度
、管壁绝对粗糙度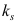 、管长
、管长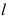 、流速
、流速![]() 、动力粘度
、动力粘度![]() 和流体密度
和流体密度![]() 有关。根据
有关。根据 定理,则可用( )个无量纲数表示上述物理现象。
定理,则可用( )个无量纲数表示上述物理现象。
A:7
B:4
C:3
D:5
答案:AI参考:答案:B。此题为管道流体中的流量和压差的关系的试题。选项中的每一个参数,除流速以外,都和管长、流体的物理性质和几何特征有关,均属于物性参数,因而都用无量纲数表示。选项A中七个无量纲数太多;选项D中只包括流速一个无量纲数,而实际上还有许多其它无量纲数也可以用来表示这一物理现象;选项C则少于题目所给的五个物性参数。所以正确的只有B选项。其中涉及的四个无量纲数包括:雷诺数Re(流速、粘度、管径之比)、努赛尔数Nu(管壁绝对粗糙度、流速、流体密度之比)、伯努利方程指数m(流速的平方和流体的密度以及重力加速度之比)、摩擦系数λ(粘度、管径、雷诺数以及管道长度和管道出口距离的压力差之比)。故选B。'
5.恒定流动中( )。
A:流动参数不随时间而变
B:速度为常数
C:加速度为零
D:流动参数随时间而变
答案:AI参考:正确答案是D流动参数随时间而变。在恒定流动中,流动参数如流量、压力、温度等都不随时间而变,这种流动是稳定的,不会发生扰动。恒定流动中的速度和加速度也是常数,但它们与时间无关。因此选项A和C是错误的。选项B虽然正确,但不是问题的正确答案。因此,答案为D流动参数随时间而变。'
6.根据量纲齐次原理,单位质量流体的伯努利方程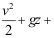 =常数,第三项的形式应为( )。
=常数,第三项的形式应为( )。
A:
B:
C:
答案:AI参考:正确答案是D:流体速度与管道直径的乘积。\n根据题干中给出的伯努利方程的式子,可以得到该方程的形式为p/ρ+ρv^2/2+ρgh=常数,根据量纲齐次原理,第三项应为流体速度与管道直径的乘积,即ρvD,所以答案为D选项。'
7.已知流动的速度分布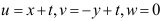 。则加速度为( )。
。则加速度为( )。
A:
B:
C:
D:
答案:AI参考:正确答案是C。\n\n根据速度分布图,可以知道速度随时间的变化率,从而得到加速度。具体来说,加速度等于速度变化量与时间的比值,即 a = Δv/Δt。根据题目给出的速度分布图,可以得出速度随时间的变化率,从而得到加速度。\n\n因此,正确答案是C。'
8.按重力相似准则设计的实验模型,长度比尺为100,模型中水深为0.1m,则原型中对应点水深和流量比尺分别为( )。
A:10m,10000
B:1m,10000
C:10m,100000
D:1m,100000
答案:AI参考:正确答案是C:10m,100000。\n根据重力相似准则设计的实验模型,长度比尺为100,模型中水深为0.1m,则原型中对应点水深为模型水深的10倍,流量比尺为模型流量与原型流量的比值,因此原型中对应点水深和流量比尺分别为10m和100000。因此,答案为C。'
9.Ma<1时,不存在马赫锥。
A:错
B:对
答案:AI参考:正确答案是B:对。\n\n马赫锥是当飞行器速度接近声速时,飞行器的前方出现圆锥状的现象,当Ma<1时,飞行器尚未达到声速,因此不存在马赫锥。所以答案是B,对。'
10.The exit pressure for an incompressible fluid jet is equal to what? ( )。
A:surrounding or atmospheric pressure
B:stagnation pressure
C:none
D:static pressure
答案:AI参考:答案:B:stagnation pressure。\r\n不可压缩流体射流出口压力等于停滞压力,其他选项周围气压或大气压、无压力、静压力都不正确。故选B。'
11.The broad subject of fluid mechanics can be generally divided into ____. ( )。
A:fluid motion and fluid dynamics
B:fluid composition and fluid dynamics
C:fluid statics and fluid dynamics
D:fluid motion and fluid stability
A:Change in pipe diameter B:Change in pressure C:Change in force exerted on the fluid D:none 13.A tank is filled with seawater to a depth of 12 ft. If the specific gravity of seawater is 1.03 and the atmospheric pressure at this location is 14.8 psi, the absolute pressure (psi) at the bottom of the tank is most nearly ( )。
A:5.4 B:27.2 C:20.2 D:26.8 14.How do the dimples on a golf ball effect drag? ( )
A:they increase drag B:none C:they reduce drag D:they do not effect drag 15.What is the material derivative used for? ( )
A:None. B:To describe the time rates of change for a given flow. C:To describe time rates of change for a given particle. D:To give the velocity and acceleration of the flow. 16.Which of the following is a good example of a non-wetting liquid when it is in contact with a glass tube? ( )。
A:beryllium B:mercury C:saltwater D:alcohol 17.An external effect is used to denote any variable that produces or tends to produce what? ( )
A:constant results B:none C:change in the system D:inaccurate results 18.The figure shows a gate made of a uniform plate of height 4 m and width 1 m, hinged about it a horizontal axis through its center of gravity, G. Depth of water on the upstream side of the plate, h is 3 m. The magnitude of the minimum force (kN) that must be applied at A to keep the gate in the vertical position is most nearly ( )。
A:26 B:66 C:41 D:22 19.A representation of a physical system that may be used to predict the behavior of the system in some desired respect is what? ( )
A:Model B:Experiments C:Prototype D:Facsimile 20.If a source and a sink are placed a short distance apart, but not on top of each other, what type of body is formed? ( )
A:A cylinder B:A Rankine oval C:A half body D:A Doublet 21.What parameter of the flow is responsible for head loss? ( )
A:the pressure head B:the shear stress on the wall C:the Darcy friction factor. D:none 22.The Weber number is a relationship between the inertial force and what other force? ( )
A:kinetic B:frictional C:gravity D:surface tension 23.The German professor Ludwig Prandtl introduced the concept of what? ( )。
A:fluid statics B:aerodynamics C:fluid mechanics D:fluid boundary layer 24.What is the symbol for the Cauchy number? ( )
A:Cn B:Ca C:Cu D:Co 25.An object weighs 275 N when fully immersed in water and 325 N when fully immersed in oil of specific gravity 0.9. The volume of the object (m3) is most nearly ( )。
A:0.02 B:0.50 C:0.20 D:0.05 26.An example of a deforming control volume is ( )
A:solid pipe B:A jet engine C:balloon D:impounding reservoir 27.Another term for the speed of sound is what? ( )。
A:absolute velocity B:relative speed C:acoustic velocity D:acoustic speed 28.A qualitative description of physical quantities can be given in terms of ____. ____
29.Kinetic energy change is often accompanied by a change in ____. ____。
30.A doublet, placed in a uniform flow, is used to represent flow around a ____. ____
31.For problems involving only two pi terms, results of an experiment can be conveniently presented in ____. ____
32.The ____ equations are the basic differential equations describing the flow of Newtonian fluids. ____
33.Models for which one or more of the similarity requirements are not satisfied are called ____ models. ____
34.Turbulent pipe flow properties depend on the fluid ____ and the ____. ____, ____
35.What type of velocity must be considered when using a moving control volume?
36.Units of ____ are used to quantify the amount of head involved. ( )
A:mass B:length C:force D:time 37.As a “rule of thumb,” a perfect gas may be considered incompressible for which range of Mach numbers? ( )。
A:less than 0.3 B:greater than 0.5 C:greater than 0.3 D:less than 0.7 38.The standard unit normal vector ( )
A:is normal to the surface pointing outwards. B:is along to the control surface. C:is tangent to the control surface. D:is normal to the surface pointing inwards. 39.Water striders are capable of covering 100 body lengths in one second. True or False? ( )
A:错误 B:正确 40.Model design conditions are also called similarity requirements or modeling laws. ( )
A:错误 B:正确 41.The number of required pi terms is fixed in accordance with the pi theorem. ( )
A:错误 B:正确 42.Variables can be classified into three general groups: geometry, material properties, and external effects. ( )
A:正确 B:错误 43.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. ( )
A:正确 B:错误 44.Distorted models cannot be successfully used, only true models can be accurately used. ( )
A:对 B:错 45.The flow of river water is significantly affected by surface tension. ( )
A:错误 B:正确 46.Geometric and Reynolds number similarity is usually not required for models involving flow through closed conduits. ( )
A:错误 B:正确 47.Work is transferred by rotating shafts, normal stresses, and tangential stresses. True or False? ( )
A:正确 B:错误 48.The Bernoulli equation can be modified for compressible flows. True or False? ( )
A:错误 B:正确 49.The amount of mass in a system is constant. True or False?( )
A:正确 B:错误 50.The drag on a ship depends on both the Reynolds number and the Froude number. ( )
A:正确 B:错误 51.A potential flow vortex is rotational. True or False? ( )
A:错误 B:正确 52.Examples of a source and a sink are a pump and a turbine. True or False? ( )
A:正确 B:错误 53.Flow meters based on the Bernoulli equation, used to measure flowrates in open channels such as flumes and irrigation ditches, include devices like the sluice gate and the sharp-crested weir. True or False? ( )
A:正确 B:错误 54.When a fluid particle travels along a curved path, a net force directed toward the center of the curvature is required. True or False? ( )
A:正确 B:错误 55.Flows in canals, rivers, spillways, and stilling basins are all examples of flows with a free surface. ( )
A:正确 B:错误 56.A straight pipe causes a greater head loss than a bent pipe. ( )
A:错误 B:正确 57.圆管内的流动状态为层流时,其断面的平均速度等于最大速度的( )倍。
A:1.0 B:2.0 C:0.5 D:1.5 58.当水的压强增加一个大气压时,水的密度增大约为( )。
A:1/2 000 B:1/20 000 C:1/1 000 D:1/4 000 59.流体处于平衡状态的必要条件是( )。
A:质量力有势; B:流体无粘性; C:流体粘度大; D:流体正压。 60.液体收到表面压强p作用后,它将( )地传递到液体内部任何一点。
A:只传递压力不传递压强 B:有所增加 C:毫不改变 D:有所减小 61.( )的流体称为不可压缩流体。
A:速度很大 B:速度很小 C:密度不变 D:忽略粘性力 62.连续性方程是( )定律在流体力学中的数学表达式。
A:质量守恒 B:牛顿内摩擦 C:能量守恒 D:动量守恒 63.文丘里管用于测量流量时的主要工作原理是( )。
A:动量方程 B:伯努利方程 C:连续性方程 D:运动方程 64.速度势函数和流函数同时存在的前提条件是( )。
A:两维不可压缩连续且无旋运动 B:三维不可压缩连续且无旋运动 C:两维不可压缩连续运动 D:三维不可压缩连续运动 65.在圆管流动中,湍流的断面流速分布符合( )。
A:抛物线规律 B:均匀规律 C:直线变化规律 D:对数曲线规律 66.沿程损失系数λ的量纲(单位)为( )。
A:无量纲 B:m/s C:m2/s D:m 67.一容器内盛有水,容器作匀速直线运动,容器内水质点所受的质量力为( )(备注:铅垂方向向上为正)。
A:ma B:-g C:0 D:mg 68.不可压缩流体的总流连续性方程Q=VA适用于( )。
A:恒定流 B:恒定流及非恒定流 C:非恒定流 D:均不适用 69.一维流动中,“截面积大处速度小,截面积小处速度大”成立的必要条件是( )。
A:粘性流体 B:可压缩流体 C:理想流体 D:不可压缩流体 70.无旋运动限于( )。
A:流线是直线的流动 B:恒定流动 C:迹线是直线的流动 D:微团无旋转的流动 71.静止流场中的压强分布规律( )。
A:仅适用于粘性流体; B:既适用于理想流体,也适用于粘性流体。 C:仅适用于不可压缩流体; D:仅适用于理想流体; 72.若流动是一个坐标量的函数,又是时间t的函数,则流动为( )。
A:一元流动 B:一元非恒定流动 C:二元流动 D:一元恒定流动 73.某点的真空压强为2m水柱高,当地大气压为1个工程大气压,则该点的绝对压强为( )。
A:-2m水柱高 B:8m水柱高 C:2m水柱高 D:其余选项答案都不对 74.湍流附加切应力是由于( )而产生的。
A:分子的内聚力 B:湍流元脉动速度引起的动量交换 C:分子间的动量交换 D:重力 75.均匀流(不考虑损失)的总水头线与测压管水头线的关系是( )。
A:互相平行的直线 B:互相平行的曲线 C:互不平行的直线 D:互不平行的曲线 76.在边界层内,具有相同量级的为( )。
A:惯性力,粘性力 B:惯性力,弹性力 C:惯性力,重力 D:惯性力,表面张力 77.实际液体恒定总流中总水头线总是沿程下降的。( )
A:对 B:错 78.粘性是流体产生水头损失的内因。( )
A:错 B:对 79.在连续介质假设下,流体的物理量( )。
A:与时间无关 B:只是时间的连续函数 C:只是空间坐标的连续函数 D:是空间坐标及时间的连续函数 80.飞机在20℃的静止空气中飞行,其马赫数 =1.5,则飞机速度约为( )。
A:500 m/s B:545m/s C:530m/s D:515 m/s 81.不可压缩流体的特征是( )。
A:温度不变 B:压强不变 C:密度不变 D:粘度不变 82.定常流动时,水平管道的截面逐渐缩小,管内水流的压强( )。
A:不改变 B:逐渐变大 C:逐渐变小 D:没有变化规律 83.翼型的绕流阻力主要来源于( )。
A:摩擦阻力 B:冲击损失 C:压差阻力 D:扩散损失 84.Re的物理意义是( )。
A:惯性力与粘性力之比 B:压力与惯性力之比 C:惯性力与迁移惯性力之比 D:惯性力与重力之比 85.平面势流的等流函数线与等势线( )。
A:斜交 B:平行 C:正交 D:重合 86.重力作用下流体静压强微分方程为dp=( )。
A:-ρdz B:-ρgdz C:ρgdz D:-gdz 87.已知大气压强为98.1kN/m2,管道内的绝对压强为117.7kN/m2时,相对压强为 ( )。
A:1.96kN/m2 B:196kN/m2 C:196N/m2 D:19.6kN/m2 88.不可压缩流体是指( )。
A:理想流体 B:忽略密度变化的流体 C:忽略黏性的流体 D:平衡流体 89.用一块平板挡住水池下部的水平输水管道的出口,当水池中的水深增加时,平板的形心与压力中心的距离(即偏心距)将( )。
A:增大 B:不变 C:减小 90.定常流动的( )加速度为0 。
A:当地 B:迁移 C:重力 D:合 91.边界层的厚度取决于( )。
A:雷诺数的大小 B:惯性力的大小 C:速度梯度的大小 D:黏性力的大小 92.圆管层流,实测管轴上流速为0.4m/s,则断面平均流速为( )。
A:0.2m/s B:0.4m/s C:0.1m/s D:0.32m/s 93.边界层外的势流区可以看作是( )。
A:粘性流体的流动 B:理想流体的流动 C:有旋流动 D:无旋流动 94.以下为表面力的是( )。
A:惯性力 B:压力 C:重力 D:粘性力 95.下列属于流体静压强基本特性的是
A:流体静压强大小与流体密度有关 B:流体静压强的方向与作用面相垂直 C:流体静压强不随时间变化 D:静止流体中任意一点流体压强的大小与作用面的方位无关。 96.压力体里( )。
A:可以有液体 B:一定没有液体 C:一定有液体 D:可以没有液体 97.速度势函数的性质为( )。
A:不可压缩流体的有势流动中,势函数f满足拉普拉斯方程 B:无旋流动中,势函数f 满足拉普拉斯方程 C:势函数f 是调和函数 D:任意曲线上的速度环量等于曲线两端点上速度势函数f值之差 98.下列属于液柱式测压计的是
A:U形管 B:倾斜微压计 C:皮托管 D:测压管 99.下列流体的作用力中,属于质量力的是( )
A:电磁力 B:粘性内摩擦力 C:惯性力 D:重力 100.普朗特认为,粘性流体绕流物体流场可以分为三个区域,分别为( )。
A:外部势流 B:过渡区 C:边界层 D:尾涡区 101.一般情况下,流体微团的运动形式包括( )。
A:角变形运动 B:旋转运动 C:平移运动 D:线变形运动 102.密度为常数的流体称作不可压缩流体。
A:对 B:错 103.均质、连通的静止液体内任何一点的测压管水头等于常数。
A:错 B:对 104.螺旋流是点涡和点汇的叠加。( )
A:对 B:错 105.连续性方程不适用于黏性流体。( )
A:对 B:错 106.定常非均匀流在有压管流中是存在的。( )
A:错误 B:正确 107.串联管路的总水头等于各管段水头损失之和。
A:正确 B:错误 108.当层流底层厚度大于绝对粗糙度,此时的管子称为水力粗糙管。
A:错误 B:正确 109.平衡流体中任意点的静压强值只能由该点的坐标位置来决定,而与该压强的作用方向无关。
A:对 B:错 110.平面流动中,通过两条流线间任一曲线单位厚度的体积流量等于两条流线的流函数之差。
A:对 B:错 111.流线和迹线实质是一回事。
A:错 B:对 112.流体力学中研究流体运动主要采用欧拉法。
A:对 B:错 113.相对压强可以大于、等于或小于零。
A:错 B:对 114.连通管中的任一水平面都是等压面。
A:错 B:对 115.并联管路中总流量等于各支管流量之和。
A:对 B:错 116.均匀流动各有效截面的平均流速相等。
A:错 B:对 117.翼型的绕流阻力主要来源于摩擦阻力。( )
A:错 B:对




