第一章测试1.A charge +Q is fixed in position as a small charge +q is brought near it and released from rest. Which best describes the magnitude of the velocity of the charge +q as r, the distance between the charges increases? ( )
A:The magnitude of the velocity will remain constant.
B:The magnitude of the velocity will increase, and its rate of increase will also increase.
C:The magnitude of the velocity will decrease, and its rate of decrease will also decrease.
D:The magnitude of the velocity will increase, but its rate of increase will decrease.
E:The magnitude of velocity will increase, but its rate of decrease will increase.
答案:D
2.The motion of large bodies at great distances is governed primarily by gravity and not by the electrostatic force because ( )
A:the electrostatic force is canceled out by the magnetic force
B:the majority of matter is electrically neutral
C:the electrostatic force is felt only over short distances
D:gravity is a much stronger force than the electrostatic force
E:of the relative scarcity of antiparticles
答案:B
3.An object with a charge of –2q feels a force of F when put at a point P in an electric field. In terms of F and q, the strength of the electric field at this point is ( ).
A:2qF
B:
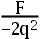
C:
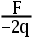
D:
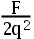
E:
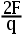
答案:C
5.Based on Gauss' Law, which of the following affects the electric flux through a Gaussian surface?( )
A:a magnetic monopole enclosed by the surface
B:a magnetic dipole outside of the surface
C:a charge moving with a constant velocity outside the surface
D:a stationary electric charge enclosed by the surface
E:a stationary electric charge outside the surface
答案:D
6.Which of the following pairs of charge distributions and Gaussian surfaces are correctly paired such that the Gaussian surface can be used to find the electric field associated with that charge distribution?( )
A:plane and sphere
B:infinite line and rectangle
C:plane and cylinder
D:infinite line and sphere
E:plane and rectangle
答案:C
7.If the electric field does positive work on a negative charge as the charge undergoes a displacement from point A to point B within an electric field, then the electrical potential energy ( )
A:is negative.
B:is positive.
C:electric fields cannot do work.
D:increases.
E:decreases.
答案:E
8.The negative derivative of electric potential with respect to radius is equal to ( )
A:potential energy
B:electric force
C:charge
D:electric field
E:capacitance
答案:D
9.The potential difference due to a finite rod along the x-axis is given by the equation V(x) = C[ln(x + L) – ln(x)], where C and L are constants. What is the electric field due to this rod? ( )
A:
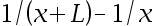
B:
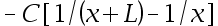
C:
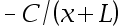
D:
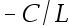
E:
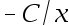
答案:B
10.
Point A is a distance L to the left of a charge Q. Point B is a distance 3L to the left of point A. If the electric field at point A due to charge Q is E, what is the electric field at point B?
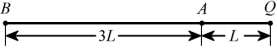
A:3E B:E C:E/9 D:E/16 E:E/3
答案:D
11.

A:
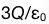 B:
B: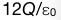 C:
C: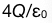 D:
D: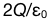 E:
E: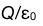
答案:A
12.
Two solid spheres, both of radius 5 cm, carry identical total charges of 2 nC. Sphere A is a good conductor. Sphere B is an insulator, and its charge is distributed uniformly throughout its volume. How do the magnitudes of the electric fields they separately create at a radial distance of 6 cm compare?
A:
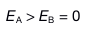 B:
B: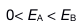 C:
C: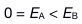 D:
D: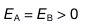 E:
E: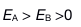
答案:D
13.

A:
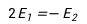 B:
B: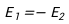 C:
C: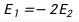 D:
D: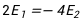 E:
E: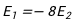
答案:E
14.
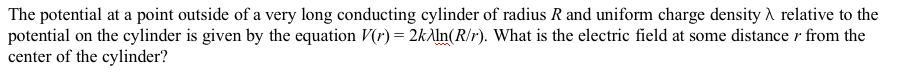
A:
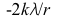 B:
B: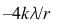 C:
C: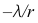 D:
D: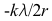 E:
E: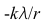
答案:A
温馨提示支付 ¥3.00 元后可查看付费内容,请先翻页预览!

