- The description and definition of the theoretical or conceptual framework cannot be linked to a presentation of the researcher’s methodology. ( )
- The proposal should set out the central aims and questions that will guide your research. ( )
- A high quality research proposal may not run the risk of being rejected simply because of your poor writing. ( )
- A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. ( )
- When you propose your research context, you should include ________. ( )
- Which of the following questions should be addressed in all research proposals? ( )
- Before writing the research proposal, you should read and conform to all ( ) you can find on the university website.
- Doctoral candidates should describe the project’s ( ) while writing a successful proposal.
- Your proposal title may vary based upon the ( ) of research you’re doing.
- In order to write a good research proposal, it is essential to be clear about its ( )
- You can put your hobbies on your CV. ( )
- There should be more than three references on your CV. ( )
- You should lie on your CV occasionally. ( )
- All of your previous jobs should be included on your CV. ( )
- Where can you get a reference from? ( )
- What order should your jobs be put in? ( )
- How long should a CV roughly be? ( )
- What should always be attached to a CV? ( )
- What should be at the top of a CV? ( )
- What coulour should a CV be typed up in? ( )
- Always customize your cover letter to the job position you are applying for. ( )
- It's okay to copy information off of your resume and paste it on your cover. ( )
- You’d better not suggest the names (and contact details) of experts who you think would be able to provide an impartial evaluation of the research described in your manuscript. ( )
- If you’re going to refer to the editor of the journal by name in your cover letter, make sure you’ve got the correct editor name/journal name/journal office address combo. ( )
- Check all of the following ways you can use to "stand out" when writing your Cover Letter. ( )
- Cover letters often begin with the applicant explaining how they ( ).
- I decided not to interview her because the ( )in her cover letter was very poor.
- While writing a cover letter for paper submission ( ) should include the title of the paper being submitted, the word count and all the authors’ names.
- It is well-known that a proper cover letter is a stepping stone and an opportunity for the author to ( ) his manuscript.
- A cover letter should be ( )
- It is considered standard formatting to include the recipient's address before the salutation in a business letter. ( )
- An "Enclosure" note should appear below the typed name of the sender at the end of the letter. ( )
- The date on a business letter should appear after the salutation. ( )
- In business letters a salutation is generally followed by a comma or a colon. ( )
- With block format, all new paragraphs are indented.( )
- Dear Ms. Marry Mee is an example of ( )
- Before you seal and send your letter, make sure to ( ) it.
- In block format, you do not need to ( ) each paragraph.
- Our address and phone number are printed on our ( ) and envelope.
- A(n) ( ) is written by an individual to deal with business of a personal nature.
- Clenching your fist to show anger or determination is an emphtic gesture. ( )
- When answering questions, you are expected to talk to the single questioner who has raised the question for you to answer instead of the entire audience. ( )
- The questioners might ask you to clarify some viewpoints that have not been fully understood or demonstrated during your speech in a question and answer session . ( )
- Using more passive verbs in your oral presentation will make your language vivid and expressive .( )
- The conclusion of your presentation usually include__________. ( )
- The opening remarks of an introduction usually consist of ________ ( )
- Conference organizations usually include_________ .( )
- When you make a comparison or contrast during your presentation, you may use the expressions “______” . ( )
- Those who attend a ________ session will read the posted papers and discuss them with the author.( )
- Which of the following visual aids is the most commonly used in an international conference presentation? ( )
- In the conclusion of your paper, you need to repeat the major arguments mentioned in the introduction. ( )
- Problems and limitations of your research shouldn’t be mentioned in the conclusion of your paper. ( )
- Contrary to the writing style in the introduction of the paper, the way of writing a conclusion is from specific to general.( )
- You need to write a long and complex conclusion with enough details in order to make the paper appear professional.( )
- When you write a conclusion for your research paper, you should follow the rules like________ ( )
- When you show the significance of your research, you may include________ ( )
- What are the essential elements that make up a conclusion? ( )
- When judging the values and significance of the study, you may use the expressions“___________”. ( )
- When restate major arguments or purpose, you may use the expressions “_________”.( )
- What’s the major function of conclusion in a paper? ( )
- When discussing th limitations of your research, make sure to _____? ( )
- When we focus on the discussion section, we mainly talk about the following elements?( )
- Which of the following expression is true? ( )
- While we summarize the main findings in the discussion section, what should be done? ( )
- Discussion section usually presents the underlying meaning of your research, which means_____?( )
- According the IMRAD format, discussion section is the _____ part of the body. ( )
- It is not necessary to discuss the reasons why you have got some unexpected data and defin their importance. ( )
- It is not necessary to identify the relationship, patterns and corralations among the received data. ( )
- The discussion section helps to engage the readers in thinking critically about issues based upon an evidence-based interpretation of findings.( )
- The discussion section can most effectively show your ability as a researcher to think critically about the issue studied. ( )
- For most research paper formats, there are the following ways to present and organize the results. ( )
- Results section includes the following elements: ( )
- Embedding a chart, a table or other non-textual elements into the paper can bring added _____to the research. ( )
- It is necessary to ______ your results in detail in the results section. ( )
- Non-textual elements are used for _____. ( )
- How to design your graphs in your journal paper?( )
- In results section, background information should be reported again in order to facilitate the comparison or contrast of those specific results.( )
- Data listed in the results section should be carefully selected and revised in the journal paper. ( )
- A chart or a table may help you highlight the important pieces of information in your paper. ( )
- Figures and tables are the main aids in illustrating the results section. ( )
- If the research material is conventional and not a specific material reported in the paper, we use ( ).
- The description of the research procedure and the various materials used in each step is usually used with ( ).
- It is a good way to identify potential problems that commonly arise with various methods. ( )
- You must include enough detail that your study can be replicated by others in your field. ( )
- In terms of Data Analysis, it tells the reader how the ( ) were analyzed.
- The three moves for writing Materials and Methods include ( ).
- Research methods in arts and science are different. ( )
- The investigation method is used to just collect materials about the current situation. ( )
- The qualitative method refers to use ( ) to process the obtained materials.
- The section of Materials and methods is a description of what was actually done. ( )
- The two types of citations are ( ).
- There are ( ) central techniques to show attitude or stance.
- To make our review cohesive, we can repeat ( ), or use some addition connectors.
- We need to avoid too much direct quoting. ( )
- When we summarize the main idea, ( ) is a good and common method.
- We must point out the shortcomings of previous works. ( )
- A well-written literature review is about a simple summary of prior works. ( )
- In the section of literature review, we collect information and sources of relevant topics from ( ), and so on.
- To organize the literature review by chronological order is to trace the development of the topic over time from the latest work to the earliest. ( )
- Literature reviews are aimed to summarize some sources and provide necessary information about a topic. ( )
- We can use logical connectives to relate the information into a whole part. ( )
- In the section of literature review, we’d better develop it from the more specific topic to the more general context. ( )
- In the part of research gap, we display the points that ( ).
- Literature review is about the ( ) studies.
- Even a broad opening needs to be clearly related to the topic. ( )
- The section of purpose clearly indicates the specific ( ) that guides the research.
- The research background is usually presented with ( ).
- Introduction tells the readers why they make the investigation, where they start, and where they intend to go to. ( )
- Which are the functions of Introduction? ( )
- Introduction leads the audience from a general topic area to a certain topic of inquiry.( )
- The ( ) part should be the second-longest part of the informative abstract ?
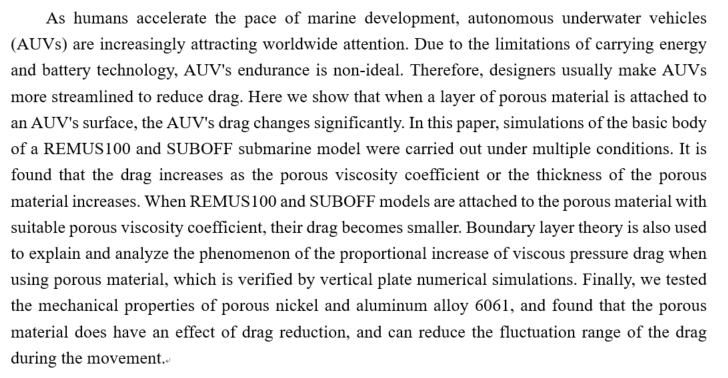
- The informative abstract includes the results and discussions of the research, but the descriptive one does not. ( )
- The descriptive abstract includes information about the purpose, scope and methods , the major findings , results and conclusions of your research.( )
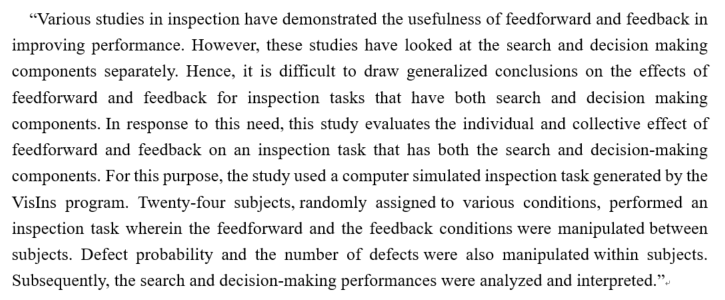
- 1) What did you do and why? 2) How did do? 3) What did you find? 4) What do the findings mean? The sequence of questions that you usually try to answer in the abstract are: ( ).
- The abstract is text-only writing. So never include Images, illustration figures and tables. ( )
- The abstract works as a marketing tool. It is selling your paper to the editors and readers, helping them to decide “whether there is something in the body of the paper worth reading”. ( )
- The abstract should express your central idea and your key points, including the ( ) of the research you discuss in the paper.
- The abstract section can work as the decided part of a research paper to be published or not. ( )
- The requirements to make a good title are: ( )
- We’d better create the final title ( ) the paper writing.
- To make the title easier to access by a computer search, we usually contain ( ) in the title.
- We usually use the parallel structure to make the title unified. ( )
- ( )is the most frequent structures occurred in the research paper titles in sciences.
- It is not good to contain keywords in the title, because they are usually too difficult to understand. ( )
- “AE and Related NDE techniques in the fracture mechanics of concrete” is not a good title, because we can never use abbreviations or acronyms in the research paper titles. ( )
- The main functions of the title are: ( )
- The general title is much better than the detailed one. ( )
- A wrong title choice can break the quality of the paper you submit. ( )
- The tone of academic writing can be very different depending on the discipline you are writing for. ( )
- Many disciplines tend to combine the results and discussion section, instead of dividing findings from interpretations of these findings. ( )
- The main purpose of the method section is to tell ( ) you did it .
- To be objective, which is the best choice in academic writing?( )
- The goal of using the IMRaD format is to present facts objectively, demonstrating a genuine interest and care /in developing new understanding about a topic. ( )
- Discussion illustrates ( )
- The Introduction tells ( ) you did the research,
- If you are writing a paper in order to answer a specific question subjectively, the IMRaD structure will most likely serve your purposes best. ( )
- Which are the features of academic ? ( )
- The structure of the journal article in all disciplines is the same.( )
- All scientific studies have limitations.
- Possible restrictions of limitations in Discussion may include______?
- "Interpreting the results" means to restate the results which the author has expressed in the Results Section.
- Implication answers the question: "Why does Discussion matter?"
- What does "R" mean in IMRaD format?
- Showing the organization of the paper can guide the readers to review the whole paper quickly.
- We should only give negative comment on previous researches.
- There are usually tenses in Introduction.
- Introduction indicates the research gap clearly.
- How many parts are there in the body part of an academic paper?
- Before starting with the outline, you need to understand a basic format you can follow while writing your research proposal.
- The length of a research proposal is about _______ pages.
- A strong introduction of a research proposal should ________.
- The research limitations indicate the flaws and shortcomings of your research, which may include _______.
- The goal of a research proposal is to describe _______.
- Visual aides may include ________ .
- In the opening remarks, you could_________by saying “I’d like to thank Professor Antonio, the Secretary General, for inviting me to deliver my speech in the conference.”
- The beginning of conference presentation usually includes: ________
- The purposes of giving academic conference presentation are _______
- Why do we attend international academic conferences?
答案:错
答案:对
答案:错
答案:对
答案:a brief overview of the general area of study within which your proposed research###a summary of the current state of knowledge and recent debates on the topic###a familiarity with the relevant field as well as the ability to communicate clearly and concisely
答案:Why do you want to do it?###How are you going to do it?###What do you plan to accomplish?
答案:instructions
答案:methodology
答案:type
答案:meaning and importance
答案:对
温馨提示支付 ¥5.00 元后可查看付费内容,请先翻页预览!

